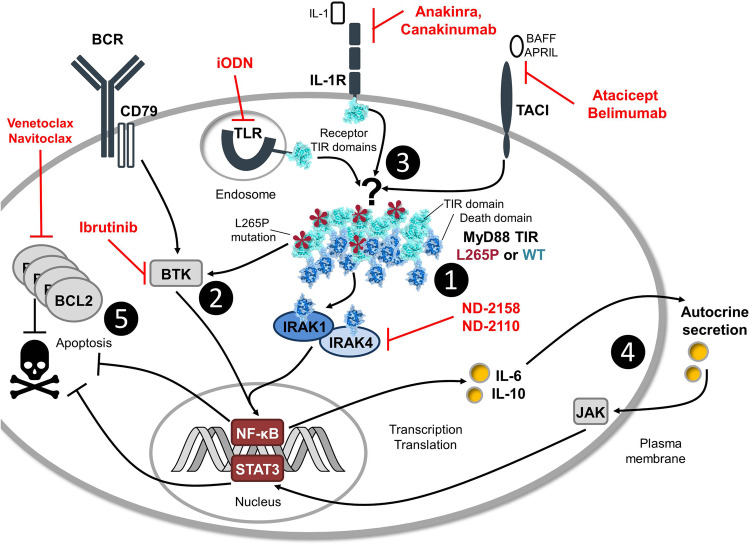
Fig. 1.
MyD88 L265P signaling networks and pharmacological targeting. MyD88 L265P, in cooperation with WT MyD88, affects multiple signaling pathways in mutated B-cells, dysregulating gene transcription and promoting survival. L265P Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domains (light blue domains with red asterisks) crosslink with WT MyD88 proteins to high molecular weight complexes, forming a scaffold of death domains (DDs, dark blue) to recruit and activate IRAK kinases (1). MyD88 L265P also binds the proximal BCR kinase, BTK, which activates NF-κB in an IRAK-independent way (2). In accordance, IRAK4 (ND-2158 & ND-2110) and the BTK inhibitor, ibrutinib [see (1) and (2) in red], affect both NF-κB and STAT3 activation. It is not known if L265P acts receptor-independently or whether signals are amplified by TLRs, IL-1R, and TACI (3). L265P-mutated cells may thus be sensitive toward inhibition of endosomal TLRs (via inhibitory oligodeoxynucleotides, iODN), IL-1R (Anakinra, Canakinumab), and TACI (Atacicept, Belimumab) receptor interference, for example, by competition with natural ligands (DNA for TLR9) or by neutralizing the ligands IL-1 and BAFF/April. Furthermore, NF-κB triggers IL-6 and IL-10 release, which might stimulate STAT3 via JAK in an autocrine way (4) and, therefore, reinforce expression of anti-apoptotic genes. High levels of BCL2 prevent apoptosis and potentiate MyD88 L265P effects on tumor cell survival (5)