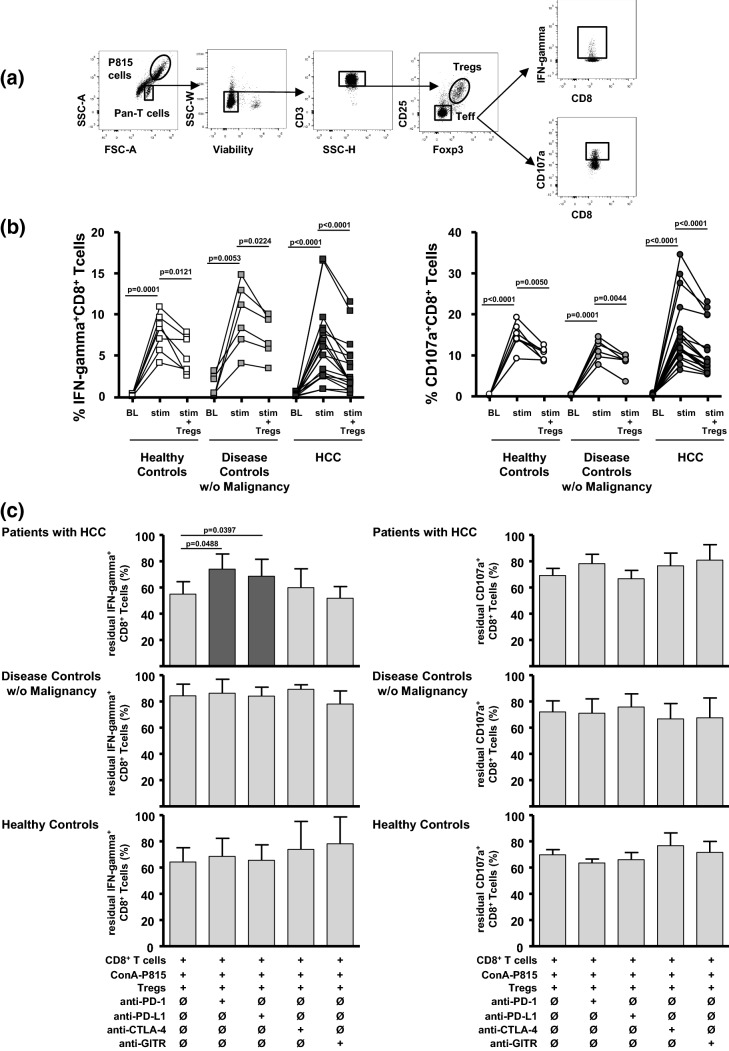
Fig. 4.
IFN-gamma production and degranulation by CD8+ T cells in lectin-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (LDCC) assays and effects of checkpoint inhibition. a The gating strategy to analyse IFN-gamma production and T cell degranulation in CD8+ T effector cells by flow cytometry in co-cultures with Con A-loaded P815 cells and Tregs (Treg to Teff ratio: 1:2). b IFN-gamma production (left) and CD107a degranulation (right) of CD8+ T effector cells in LDCC assays before (BL), with exposure to Con A-loaded P815 target cells (stim = peak secretion) and upon adding Tregs (stim + Tregs). Adding autologous Tregs reduced P815-induced peak IFN-gamma secretion and degranulation of CD8+ T cells in all study groups. p values refer to significances obtained by paired Student t test marked by bars. c Provides the summary statistics concerning the differences of IFN-gamma-production (left) and CD107a degranulation (right) by CD8+ T cells after sequential addition of Con A-loaded P815 target cells and autologous Tregs (Treg to Teff ratio: 1:2), as well as in the presence of added neutralizing anti-PD-1, anti-PD-L1, and anti-CTLA-4, and anti-GITR (10 µg/ml each). Columns represent the mean ± SD of 6–18 different donors. Anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1—but not anti-CTLA-4 nor anti-GITR—partially reversed Treg-associated inhibition of IFN-gamma secretion in CD8+ T cells from patients with HCC. Treg-mediated inhibition of T cell degranulation was not reversed by any of the antibodies. p values refer to significances obtained by paired Student t test marked by bars