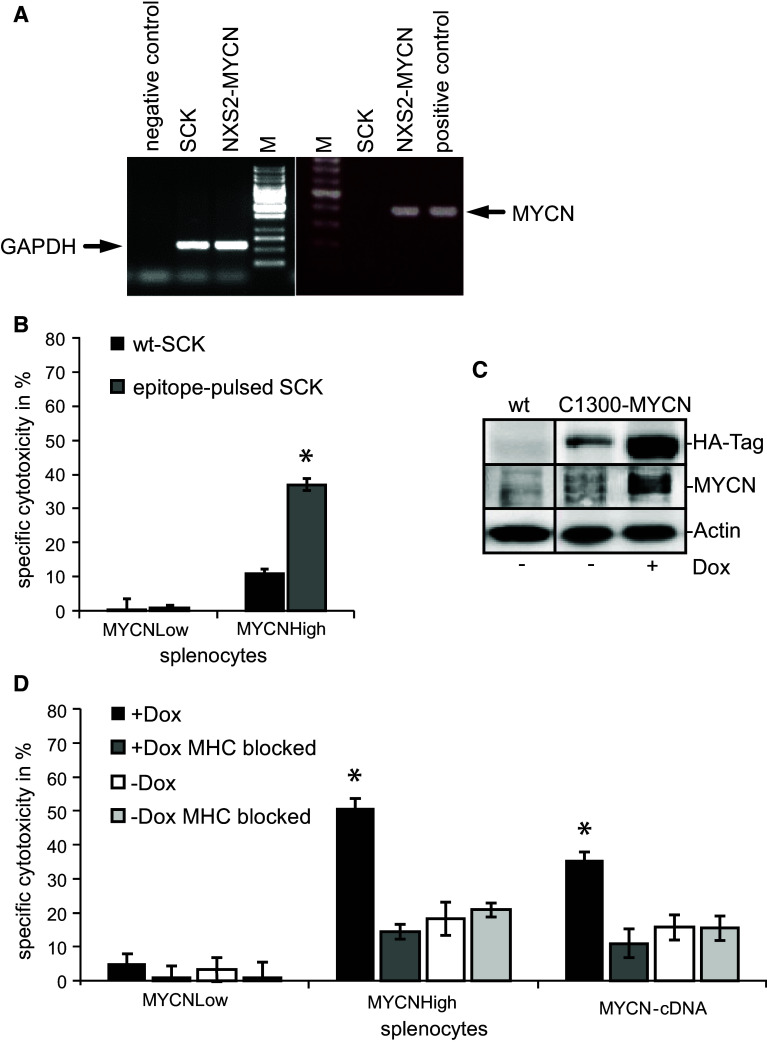
Fig. 6.
Analysis of the mediated immune response and the MYCN specificity. a Differential MYCN expression in NXS2-MYCN and SCK mammary carcinoma cells. mRNA from both cells was isolated followed by reverse transcription and MYCN-specific PCR. GAPDH served as control. b MYCN epitope specificity was analyzed with splenocytes of immunized and control mice stimulated with IL-2 for 5 days. Cytotoxic activity against wt-SCK cells (black bars) or SCK cells pulsed with the three specific MYCN epitopes (gray bars) was analyzed in 51Cr release assays (E/T ratio 60:1) (mean in % ± SD, n = 3, *p < 0.005). c Western blot analysis of C1300-MYCN cells demonstrates a high transgene expression while treated with Dox (6 h) and a low expression in the absence of Dox. d MHC class I antigen molecule H2-Kk expressed on C1300-MYCN target cells was blocked by addition of anti-H2-Kk antibodies in cytotoxicity assays with (E/T ratio 50:1) (dark and light gray bars) while incubated in the absence (white and light gray bars) or presence (black and dark gray bars) of doxycycline. Black bars indicate unblocked cells. As effector cells, splenocytes from MYCNHigh-, MYCN-cDNA- and MYCNLow-treated NXS2-MYCN mice were isolated and stimulated for 5 days with IL-2. Differences in specific cytotoxicity (in % ± SD, n = 3) were statistically significant (*p < 0.05)