Fig. 3.
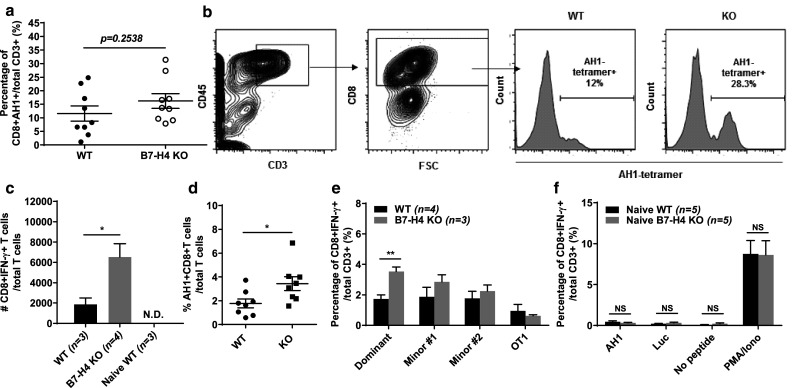
B7-H4 deficiency augments tumor-associated T cell immunity. a Ex vivo tumors were stained with AH1 tetramers to determine percentage of AH1-specific T cells at 3 weeks post injection. b Gating strategy for detection of AH1-tetramer+CD8+ T cells in the tumor. c Ex vivo cells from the draining lymph node of tumor-bearing WT, KO, or naïve mice were acutely stimulated in vitro for 5 h with 10 µg/ml of AH1 peptide in the presence of GolgiPlug (BD). Cells were then collected and stained to determine the absolute number of CD8+IFN-γ+T cells. d Splenocytes from WT and KO tumor-bearing mice cultured for 7 days with IL-2 and AH1 peptides in vitro prior to staining with AH1-tetramers. e Splenocytes were acutely stimulated in vitro for 5 h with 10 µg/ml of luciferase peptides corresponding to the dominant or minor epitopes (#1 and 2), or with irrelevant control peptide (OT1) in the presence of GolgiPlug. Cells were then stained to quantitate the percentage of CD8+IFN-γ+ T cells. f Splenocytes from naïve WT (n = 3) or KO (n = 3) mice were stimulated for 5 h with luciferase (dominant epitope) or AH1 peptides, or with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of GolgiPlug. Cells were then stained to quantitate the percentage of CD8+IFN-γ+T cells. Data presented as mean ± standard error. The presented data were either pooled from two to three experiments, or represent two or more independent experiments with similar results. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001
