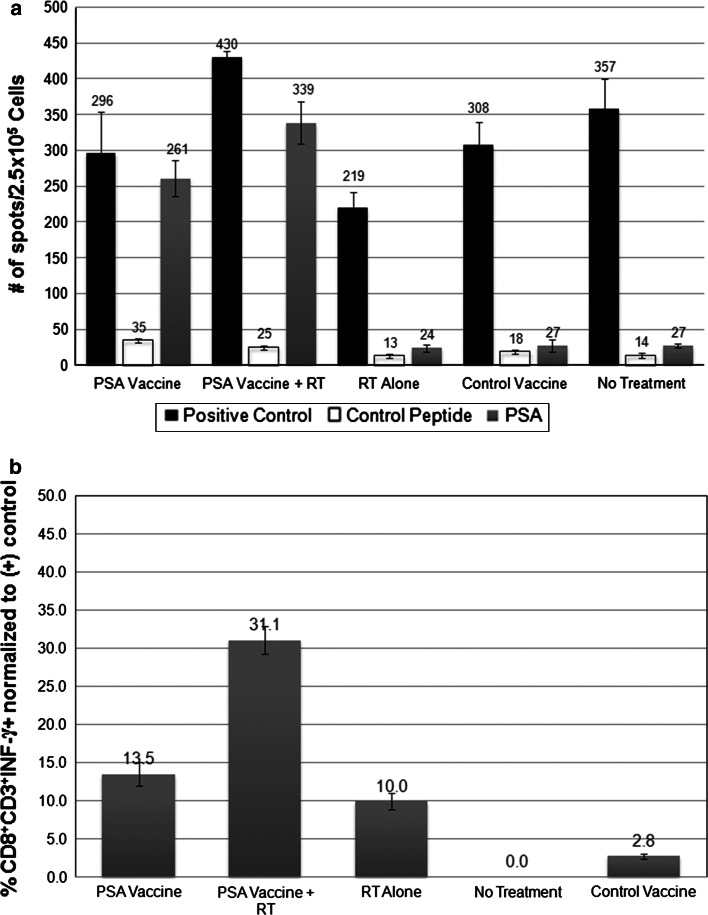
Fig. 4.
Increased Interferon-γ releasing splenic PSA-specific T cells in mice treated with combined RT and Listeria PSA vaccine, ADXS31-142 vaccine. Splenocytes from mice of each cohort were stimulated with either PSA65–74 peptide, control peptide, or a mixture of PMA and Ionomycin. The release of Interferon-γ from PSA-specific T cells was detected by ELISpot (a) and intracelluar cytokine staining assay (b). PMA and Ionomycin are non-specific activators of lymphocyte and serves as positive control for both assays. The number of IFN-γ releasing T cells per 2.5 × 105 splenocytes is shown in ELISpot assay (a) while the percentage of CD8+CD3+IFN-γ cells (normalized to the positive control) is shown in intracelluar cytokine staining assay (b)