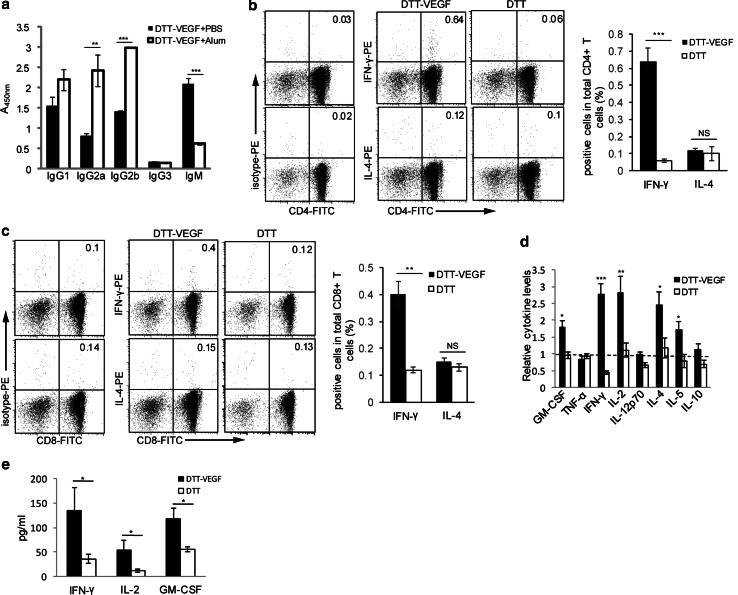
Fig. 4.
DTT-VEGF immunization induces type 1 immune response. a C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) were immunized with DTT-VEGF formulated with Alum or PBS three times at 2-week intervals, and sera were collected one week after the last immunization. Ig subclass was determined by ELISA. ***p < 0.001; **p < 0.01, Student’s T test. b, c C57BL/6 mice (n = 3) were immunized with DTT-VEGF or DTT, respectively, at 2-week intervals. One week after the third immunization. CD4+ (b) or CD8+ (c) T cells were purified from the immunized mice and then were cocultured with irradiated DCVEGF in the presence of GolgiStop; 6 h later, the cells were harvested and stained with anti-CD4-FITC or anti-CD8-FITC Ab. After permeabilization, the cells were stained for intracellular cytokine and analyzed by flow cytometry. The value in each panel represents the percentage of cytokine-producing cells in the total CD4+ or CD8+ T cell population. ***p < 0.001, **p < 0.01. Student’s T test. d, e C57BL/6 mice (n = 5) were immunized with DTT-VEGF or DTT, respectively, at 2-week intervals. One week after the third immunization, the mice were challenged with 1 × 105 B16-F10 tumor cells. Sera were collected 1 d before and 14 d after tumor challenge, and the cytokines levels were quantified using Luminex technology. The relative cytokine levels before tumor challenge were defined as the fold change compared to the unimmunized mice (d). The type 1 cytokine levels in the sera after tumor challenge are shown in e. *p < 0.05, Mann–Whitney U test. One representative experiment of two is shown