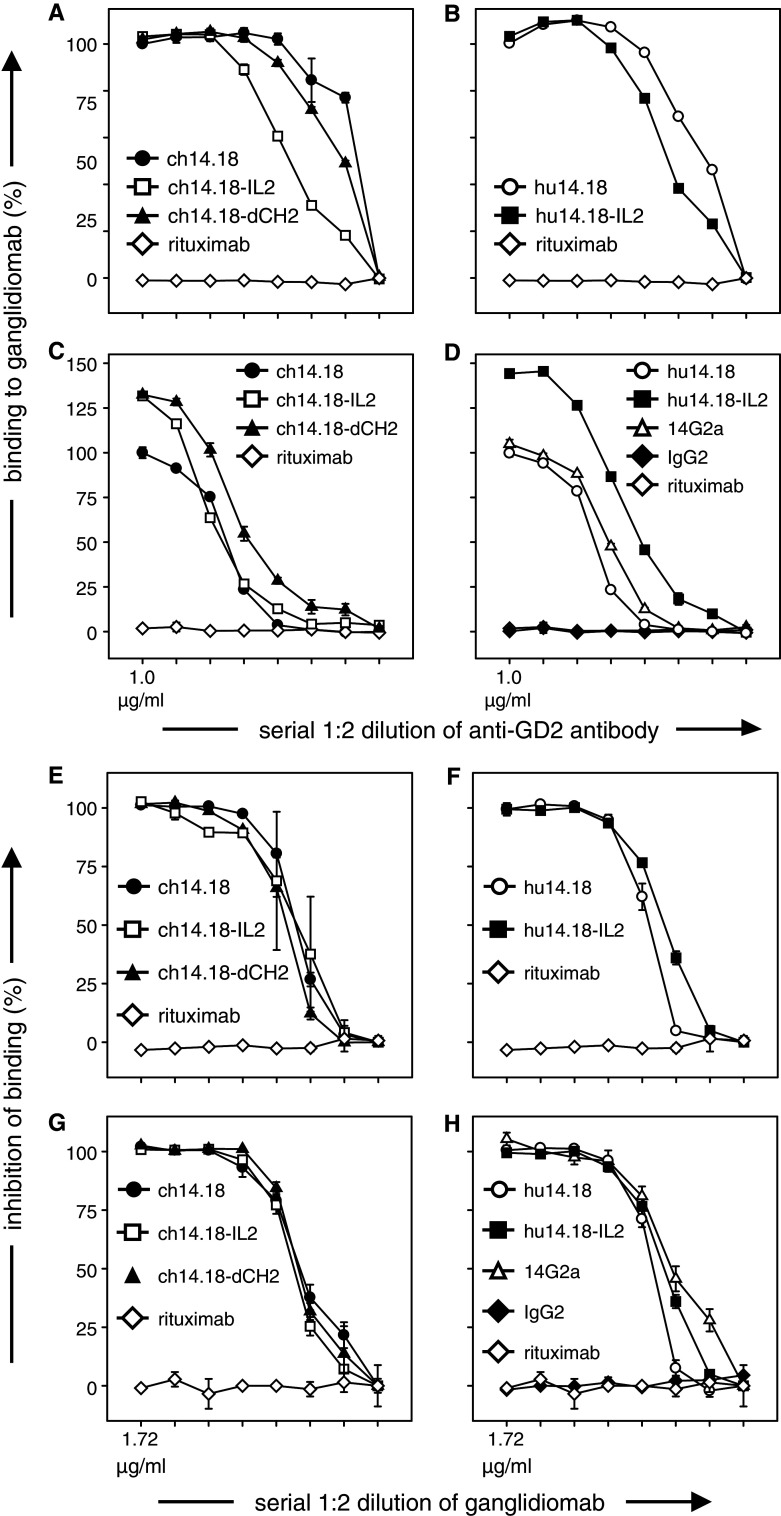
Fig. 1.
Binding of anti-GD2 antibodies to ganglidiomab and competitive binding to nominal antigen GD2. Binding of anti-GD2 antibodies of the 14.18 family to ganglidiomab was analyzed by two ELISA variants using anti-human HRP-conjugated IgG antibody (a, b) and biotinylated ganglidiomab (c, d) as secondary antibodies, respectively, as described in “Materials and methods.” ELISA signals observed with 1 μg/ml ch14.18/CHO were defined as 100 % binding. Data are expressed relative to binding of ch14.18/CHO antibody and are expressed in mean values ± SD of experiments performed in triplicates. Differences between GD2 antibodies and controls were statistically significant (*p < 0.01). Competitive binding inhibition of anti-GD2 antibodies of the 14.18 family to GD2 by ganglidiomab was analyzed by two ELISA variants, using anti-human HRP-conjugated IgG antibody (e, f) and biotinylated ganglidiomab (g, h) as secondary antibodies for detection, respectively, as described in “Materials and methods.” Data represent percent binding inhibition and are shown in mean values ± SD of experiments performed in triplicates. Differences between GD2 antibodies and controls were statistically significant (*p < 0.01)