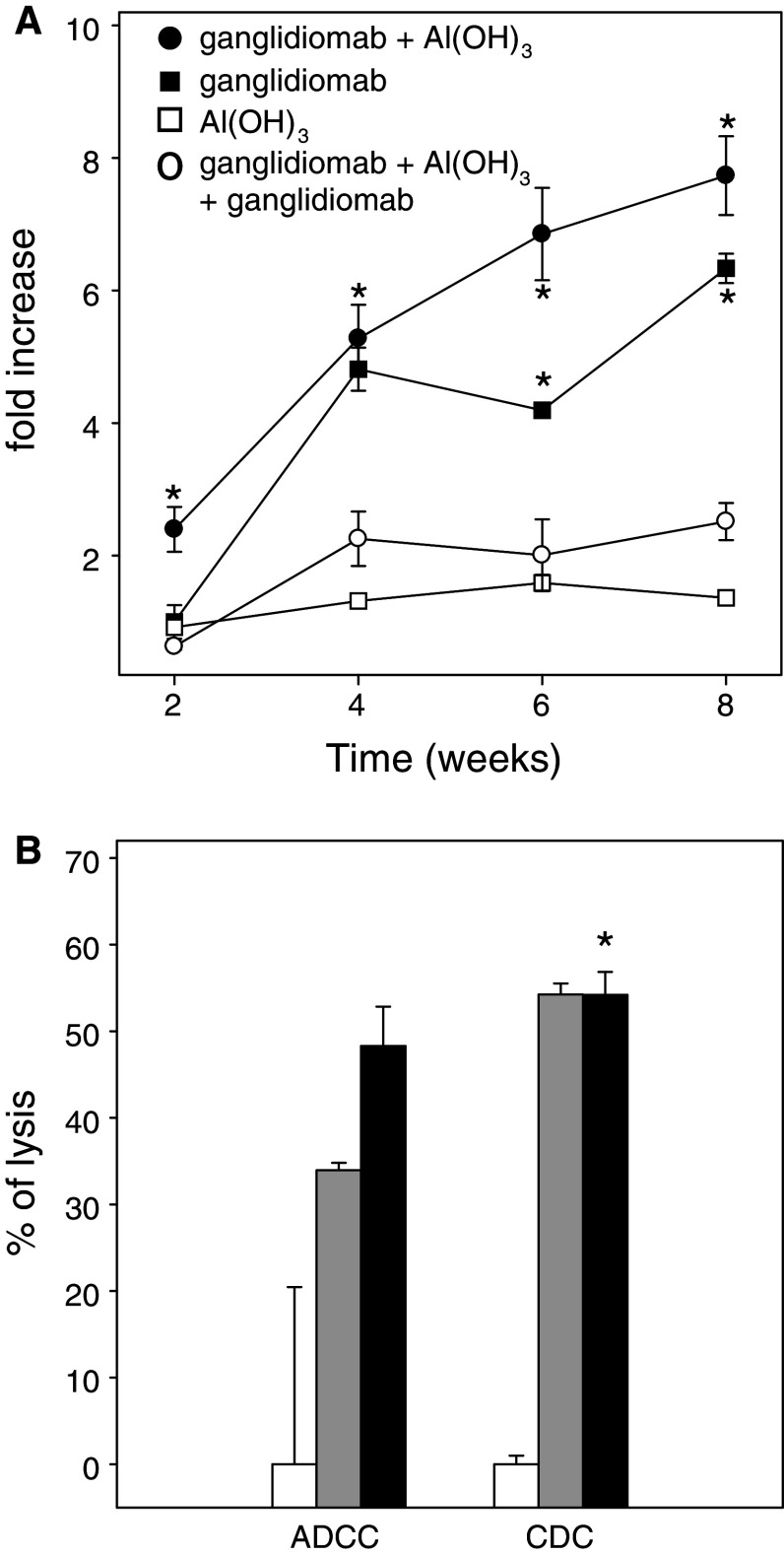
Fig. 5.
GD2-specific humoral immune response following immunization with ganglidiomab. Groups of female A/J mice (n = 7) were immunized at 2-week intervals with ganglidiomab alone or in combination with Al(OH)3 adjuvant and compared to Al(OH)3 adjuvant controls. Serum samples were taken before the first and after each immunization. Sera sampled at each time point of the respective mouse group were pooled and analyzed by GD2 solid-phase ELISA (a), antibody-dependent cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) (b). a The induction of GD2-specific antibodies following vaccination with ganglidiomab with (closed circles) and without Al(OH)3 adjuvant (closed squares) compared to Al(OH)3 adjuvant alone (open squares) was analyzed by GD2 ELISA. Data are expressed as fold increase relative to OD values measured at the start of immunization and represent mean ± SE. In order to prove GD2 specificity of observed responses, serum samples from mice immunized with ganglidiomab-Al(OH)3 were incubated prior to the GD2 ELISA with excess ganglidiomab. Differences between groups of mice immunized with ganglidiomab with or without AL(OH)3 adjuvant and controls as well as sera of ganglidiomab-Al(OH)3 group pre-treated with excess ganglidiomab (1 mg) were statistically significant (t test; *p < 0.05). b Cytotoxicity mediated by ADCC and CDC induced by serum of mice immunized with ganglidiomab with (black column) or without (gray column) adjuvant Al(OH)3 are expressed as percent of target cell lysis relative to the control group receiving Al(OH)3 adjuvant alone (white column). Data represent mean ± SE. Differences between sera of immunized mice and controls were statistically significant (t test; *p < 0.05)