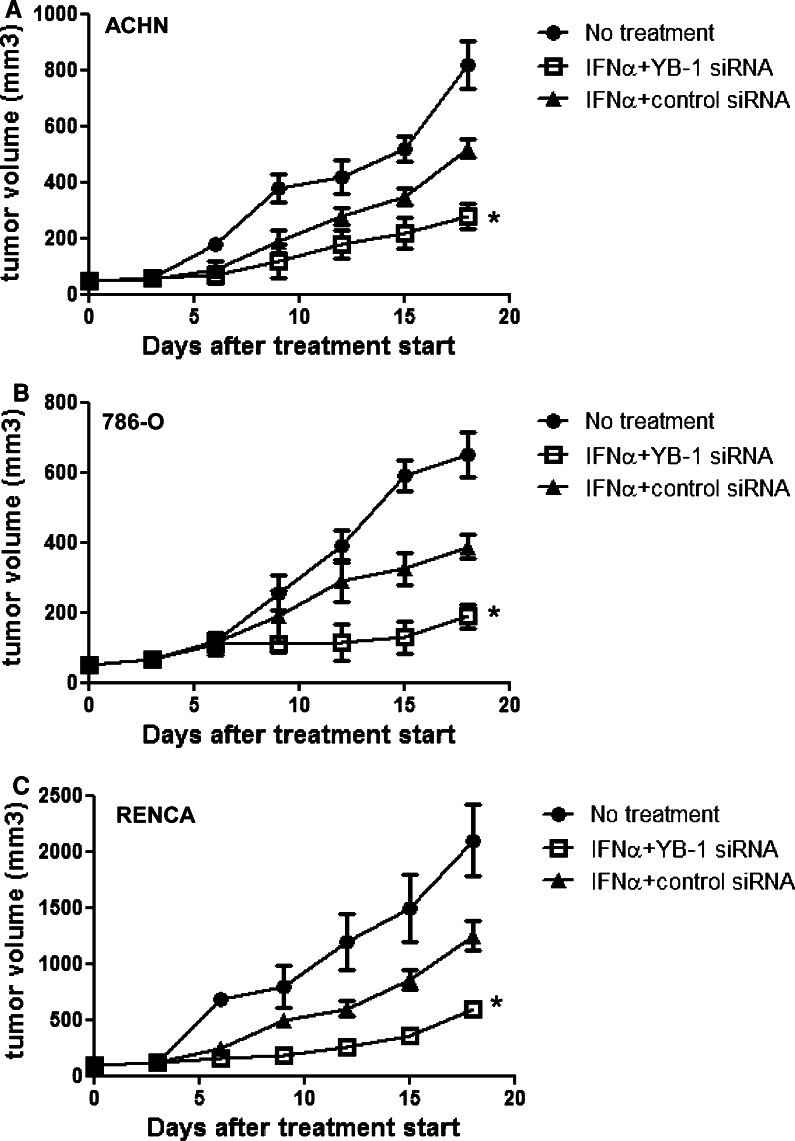
Fig. 4.
Antitumor effects of YB-1 siRNA on IFN-α in a mouse model. ACHN, 786-O cells (5.0 × 107), and RENCA (5.0 × 106) were inoculated subcutaneously (s.c.) into the shaved lateral flanks of the mice. After establishment of tumor, 15 mice were randomly divided into three groups. IFN-α was administered intraperitonelly, once a day, for 15 days. YB-1 siRNA or control siRNA was administered by s.c injection, once every 3 days, for 15 days. The sizes of primary tumors were determined every 2 or 3 days using calipers. a, b Athymic nude mice were subcutaneously implanted with ACHN and 786-O tumors, and treatment with HLBI and/or YB-1si RNA was initiated when tumors were established (*P < 0.05 compared with other 2 groups). c BALB/c mice were subcutaneously implanted with RENCA tumors (5.0 × 106) and treatment with mIFN-α and/or YB-1 siRNA was initiated when tumors were established (*P < 0.05 compared with other 2 groups)