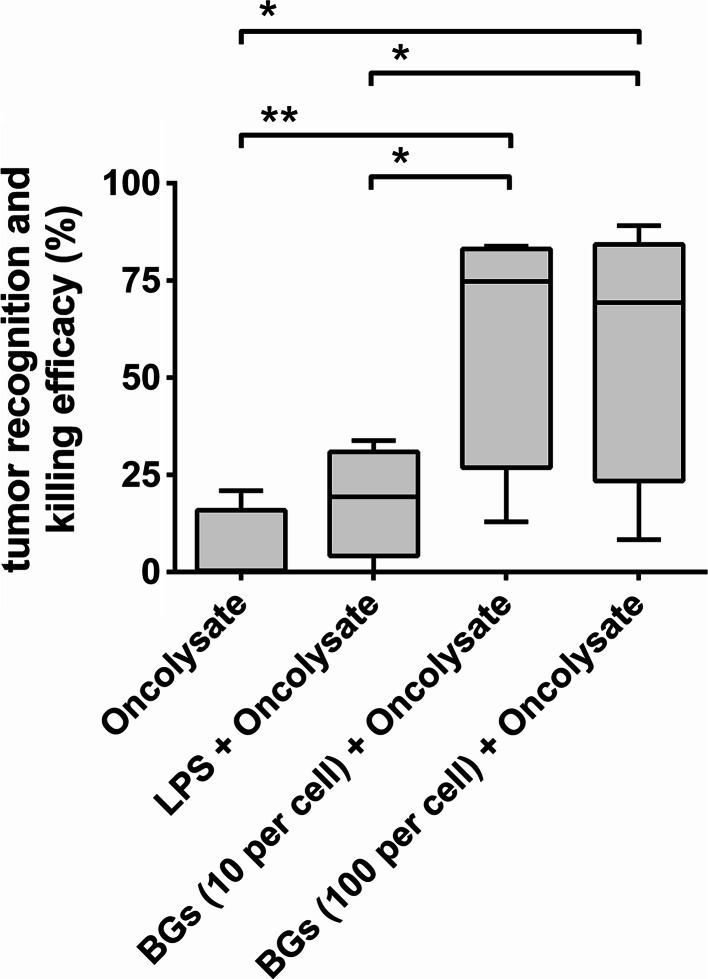
Fig. 4.
Recognition of cancer cells and cytotoxic effects of autologous T cells induced by DCs activated with oncolysates and bacteria-derived stimuli. Autologous T cells were incubated for 6 days in the presence of DCs briefly (4 h) activated with oncolysates prepared from T98G cancer cells combined with pure LPS (200 ng/mL), BGs from E. coli Nissle 1917 (10 and 100 BGs/1DC) or without extra maturation stimuli. Subsequently, stimulated T cells (effector cells; E) were added to fresh CFSE-labeled T98G cancer cells (target cells; T) at the ratio of E/T—10:1. Specific lysis of cancer cells was determined 24 h after mutual co-incubation by flow cytometry. The percentage of tumor recognition and killing efficacy was calculated as described in the Materials and methods. Box-and-whisker plots of data obtained in four independent experiments from different normal healthy donors are shown. Boxes represent interquartile ranges; the horizontal bar within each box indicates the median; whiskers show the minimum and the maximum. P values <0.05 were considered significant and are indicated with asterisks (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01)