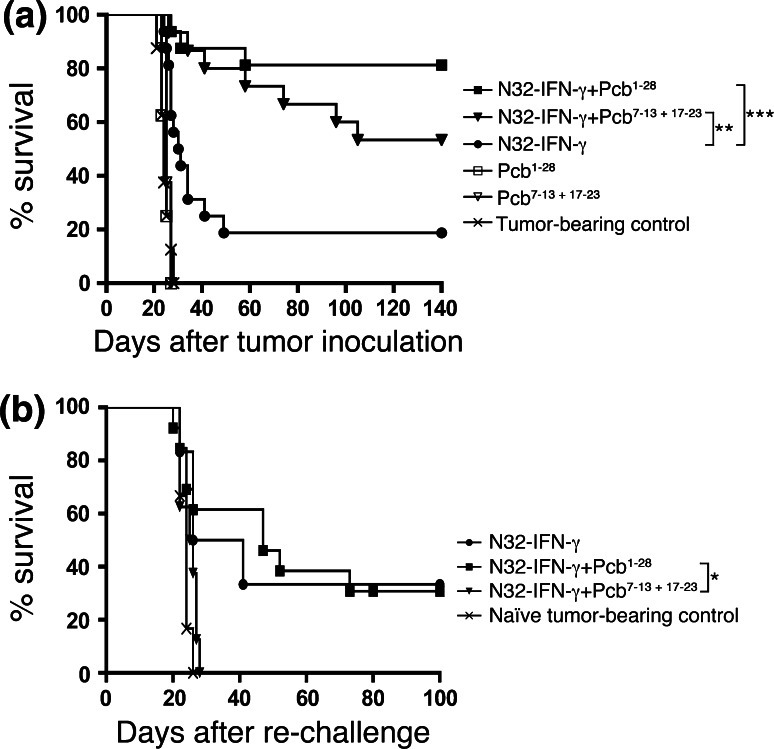
Fig. 3.
Continuous COX-2 inhibition (parecoxib) enhances the IFN-γ-based immunotherapy and induces a long-term memory. a 3 × 103 N32 tumor cells were inoculated i.c. into rats, and the animals were immunized s.c. on day 1, 15, and 29 with 3 × 106 irradiated N32-IFN-γ cells. Mini-osmotic pumps loaded with parecoxib (Pcb) (5 mg/kg/day) were implanted i.p. on day 1 (28-day pumps), or on day 7, and 17 (7-day pumps), and the animals were killed when neurological symptoms appeared. Groups include 15–16 animals except Pcb1–28, Pcb7–13 + 17–23, and tumor-bearing controls; n = 8. Groups were compared with the N32-IFN-γ group using Log-rank test, and the survival rate was significantly increased in animals treated with N32-IFN-γ + Pcb1–28 (81% cure rate; P < 0.001) as well as N32-IFN-γ + Pcb7–13 + 17–23 (53% cure rate; P < 0.01). b Rats surviving the first tumor challenge were re-challenged with a second tumor (3 × 103 N32 cells) in the opposite hemisphere without further treatment at least 170 days after the first challenge. The animals were killed when neurological symptoms appeared. Groups include 6–13 animals (tumor-bearing control and N32-IFN-γ n = 6; N32-IFN-γ + Pcb7–13 + 17–23 n = 8; N32-IFN-γ + Pcb1–28 n = 13). Groups were compared with the N32-IFN-γ + Pcb7–13 + 17–23 group using Log-rank test, and the survival was significantly increased in the N32-IFN-γ + Pcb1–28 group (P < 0.05)