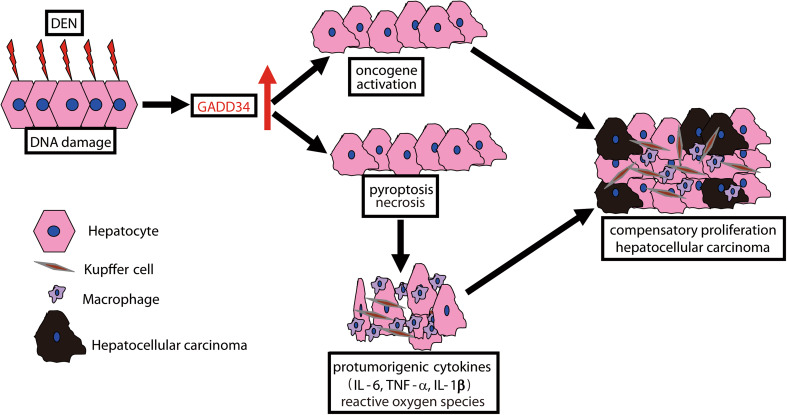
Fig. 6.
Schematic summary of this study. The chemical carcinogen diethylnitrosamine (DEN) led to DNA damage that in turn could enhance GADD34 upregulation. GADD34 augmented oncogene activation and the death of DEN-exposed hepatocytes through both pyroptosis and necrosis pathway. This process led to Kupffer cell/macrophage activation and immune cell infiltration that subsequently produced pro-tumorigenic cytokine and ROS, thereby stimulating the compensatory proliferation of surviving, mutant hepatocytes. Finally, abnormal proliferation enhanced HCC progression