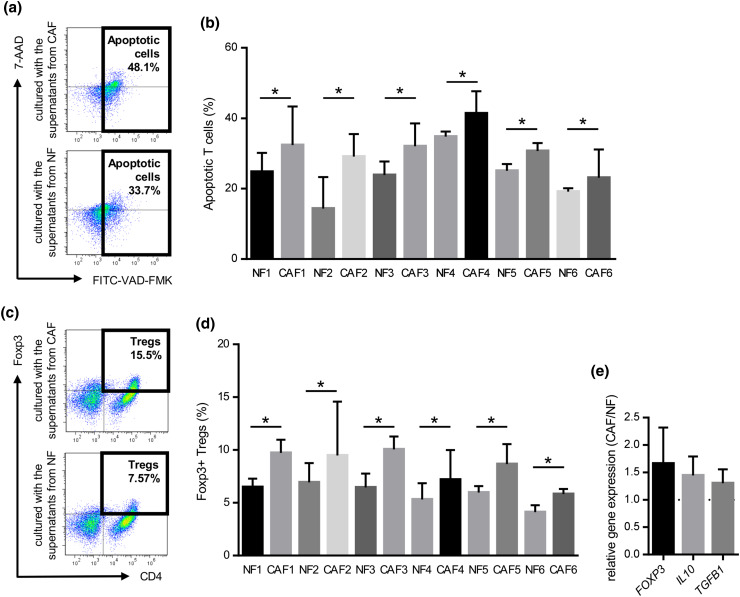
Fig. 4.
Induction of T cell apoptosis and Treg (CD4+Foxp3+) in PBMCs co-cultured with the supernatant from CAFs or NFs. PBMCs prepared from healthy donors were cultured with the supernatant from CAFs or NFs for 3 days with an anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulus, and subsequently analyzed by flow cytometry. They were stained with FITC-VAD-FMK, APC-CD3, and 7-amino-actinomycin D (7-AAD), and CD3+ T cells were gated. a Representative data of apoptotic T cells cultured with CAFs or NFs. b The induction of T cell apoptosis was significantly greater by CAFs from the six HNSCC patients tested than by NFs. Bars indicate mean values derived from 6 independent experiments. Asterisk indicates significant difference (P < 0.05) between NFs and CAFs. PBMCs prepared from healthy donors were co-cultured with the supernatant from CAFs or NFs for 4 days with an anti-CD3/anti-CD28 stimulus. They were stained with PE-Foxp3 and APC-CD4, and then analyzed by flow cytometry. They were also analyzed by real-time qRT-PCR after a 3-day incubation. c Representative data of CD4+Foxp3+Tregs in PBMCs co-cultured with the supernatant from CAFs or NFs. d The induction of T reg was significantly greater by CAFs from the six HNSCC patients tested than by NFs. Bars indicate mean values derived from 6 independent experiments. Asterisk indicates significant difference (P < 0.05) between NFs and CAFs. e The expression levels of Treg-related genes including FOXP3, TGFB1, and IL10 in PBMCs co-cultured with the supernatant from CAFs was higher than those co-cultured with the supernatant from with NFs