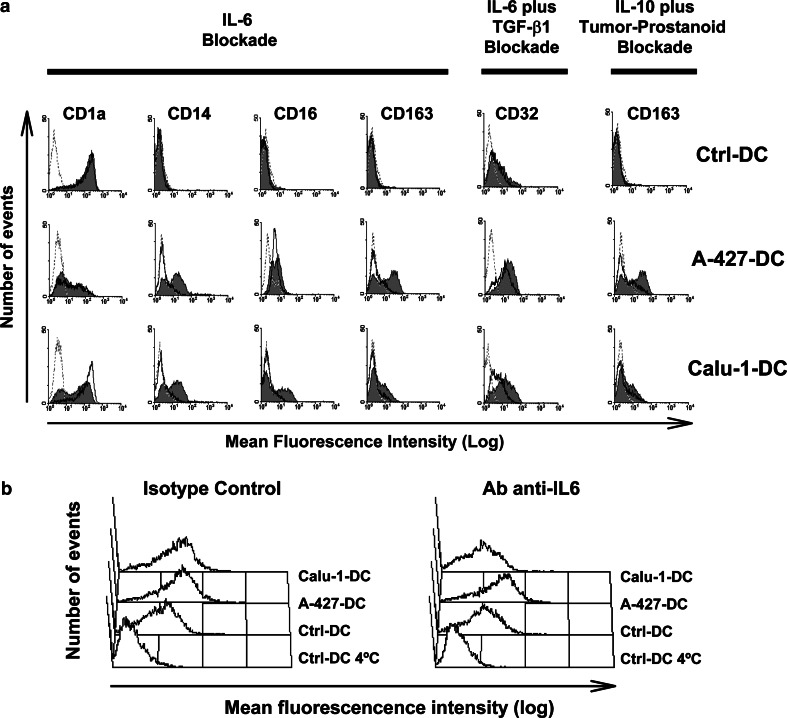
Fig. 6.
a, b Effect of IL-6, IL-10, TGF-β1, and tumor-derived prostanoids on DC phenotype and endocytic activity. Monocytes were cultured for 6 days with GM-CSF and IL-4, in the presence of PBMC-CM (Ctrl-DC), AD-CM (A-427-DC) or SCC-CM (Calu-1-DC). At the beginning of cultures, anti-IL-6, anti-IL-10, or anti-TGF-β1 neutralizing mAb, and their corresponding isotype-matched control mAb, were added. Tumor-derived prostanoid blockade was achieved by incubating tumor cell lines with indomethacine for 24 h. Control CM for these supernatants was obtained from PBMC after the same treatment. Cells received the treatments alone or in combination. a Surface marker expression of cells treated with isotype-matched control mAb and/or indomethacine-PBMC-CM (solid gray histograms) or with neutralizing mAb and/or indomethacine-tumor-CM (empty black histograms). Treatments and the markers analyzed are indicated on the top. Dotted histograms represent the fluorescence of an irrelevant isotype-matched control mAb for each marker. Shown is a representative experiment out of three. b Day-6 monocyte-derived cells cultured as above were incubated with FITC-dextran for 30 min at 37°C or at 4°C (as a control). After washing, fluorescent cells were evaluated by flow cytometry. Treatment of the cells is indicated on the top. Histograms are representative of one of two independent experiments