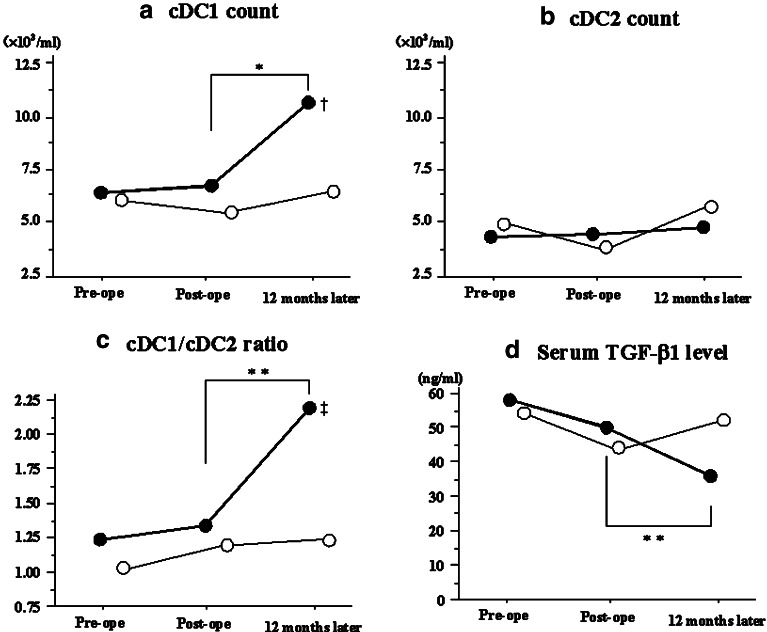
Fig. 4.
Normalized cDC1 count, cDC1/cDC2 ratio and Serum TGF- β1 level at 12 months after pancreatectomy in disease-free patients. These figures are expressed as the changes in parameters between the time of discharge and 12 months after pancreatectomy. a The cDC1 count in patients who remained disease free after 12 months significantly increased at 12 months after pancreatectomy compared to that of the postoperative period (P=0.001), however, that in patients with recurrence or metastasis did not increase. The cDC1 count in disease-free patient at 12 months after pancreatectomy was significantly higher than that in relapsed patients. (P=0.005). b The cDC2 count remained stable during the monitored period, regardless of the disease status (P=0.824). c The cDC1/cDC2 ratio in patients who remained disease free after 12 months significantly increased at 12 months after pancreatectomy compared to that of the postoperative period (P=0.011), however that in patients with recurrence or metastasis did not increase. ‡ The cDC1/cDC2 ratio in disease-free patient at 12 months after pancreatectomy was significantly higher than that in relapsed patients. (P=0.019). d The serum levels of TGF- β1 in patients who remained disease free after 12 months significantly decreased at 12 months after pancreatectomy compared to those of the postoperative period (P=0.013), whereas those in patient with recurrence slightly increased at 12 months after pancreatectomy. Disease-free patients: closed circles, Relapsed patients: Open circles. Symbols represent the median. *P<0.01, ** P<0.03 compared to postoperative period in disease-free patients. † P<0.01, ‡ P<0.03 versus relapsed patients. Statistical significance was determined using the Wilcoxon signed-rank test and the Mann–Whitney U test