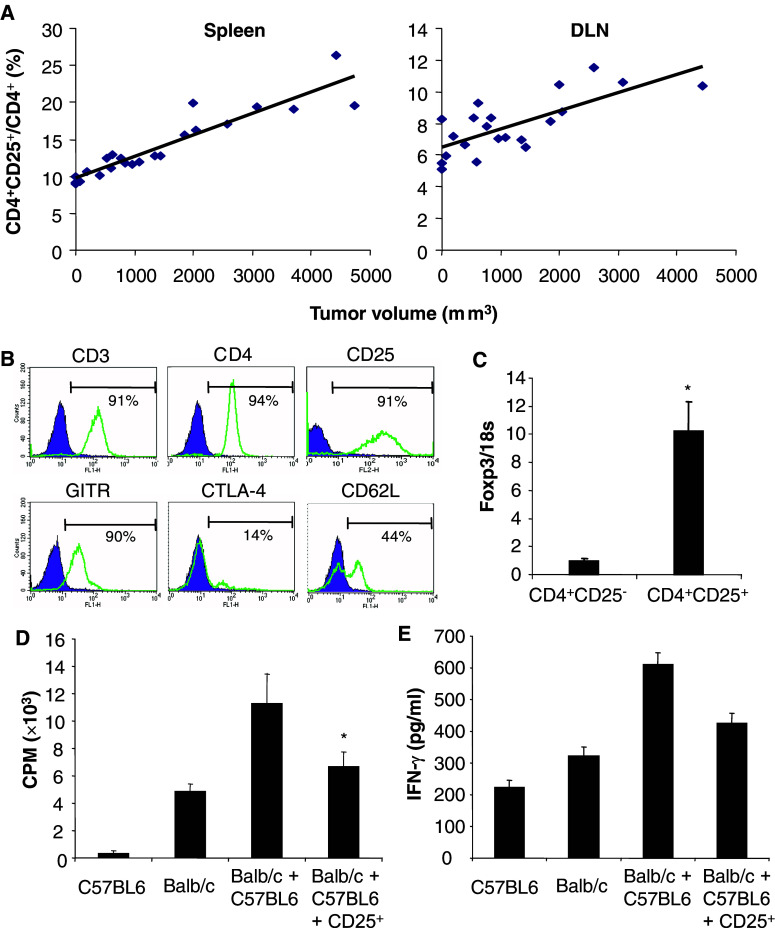
Fig. 1.
Characteristics of CD4+CD25+FoxP3+ regulatory T cells in mice bearing established 12B1 tumors. a Increase in the ratio of CD4+CD25+ to total CD4+ during tumor progression. Total splenocytes (Spleen) or draining lymph node (DLN) cells from mice bearing established 12B1 tumors at different stages were analyzed. The ratio CD4+CD25+/CD4+ was determined for each individual mouse and reported as a function of the tumor volume (r 2=0.9270, P<0.00005 in the spleen and r 2=0.7364, P<0.0005 in the draining lymph nodes). b Phenotype of CD4+CD25+ T lymphocytes purified using magnetic cell sorting from the spleen of mice bearing established 12B1 tumors (2,000–3,000 mm3). The percentage of positive cells is indicated. c Foxp3 mRNA levels are increased in CD4+CD25+ T cells purified from the spleen of mice bearing established tumors. Expression levels (average ± SD) relative to 18S ribosomal RNA are shown (*P<0.01). d Inhibition of the proliferation of allogeneic splenocytes by CD4+CD25+ T cells from tumor-bearing mice. Responder BALB/c splenocytes (Balb/c) were stimulated with C57BL6 splenocytes (C57BL6) in presence or absence of CD4+CD25+ T cells (CD25+) isolated from the spleen of mice bearing 12B1 tumors. The data are shown as mean ± SD of quadruplicate wells of 3[H]thymidine incorporation. e CD4+CD25+ T cells from tumor-bearing mice inhibit IFN-γ production. The culture supernatants of the experiment described in d were collected and IFN-γ concentration was determined by ELISA. The results are shown as the mean of duplicate wells. Asterisk is a significant difference when compared to control without CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells (P<0.01)