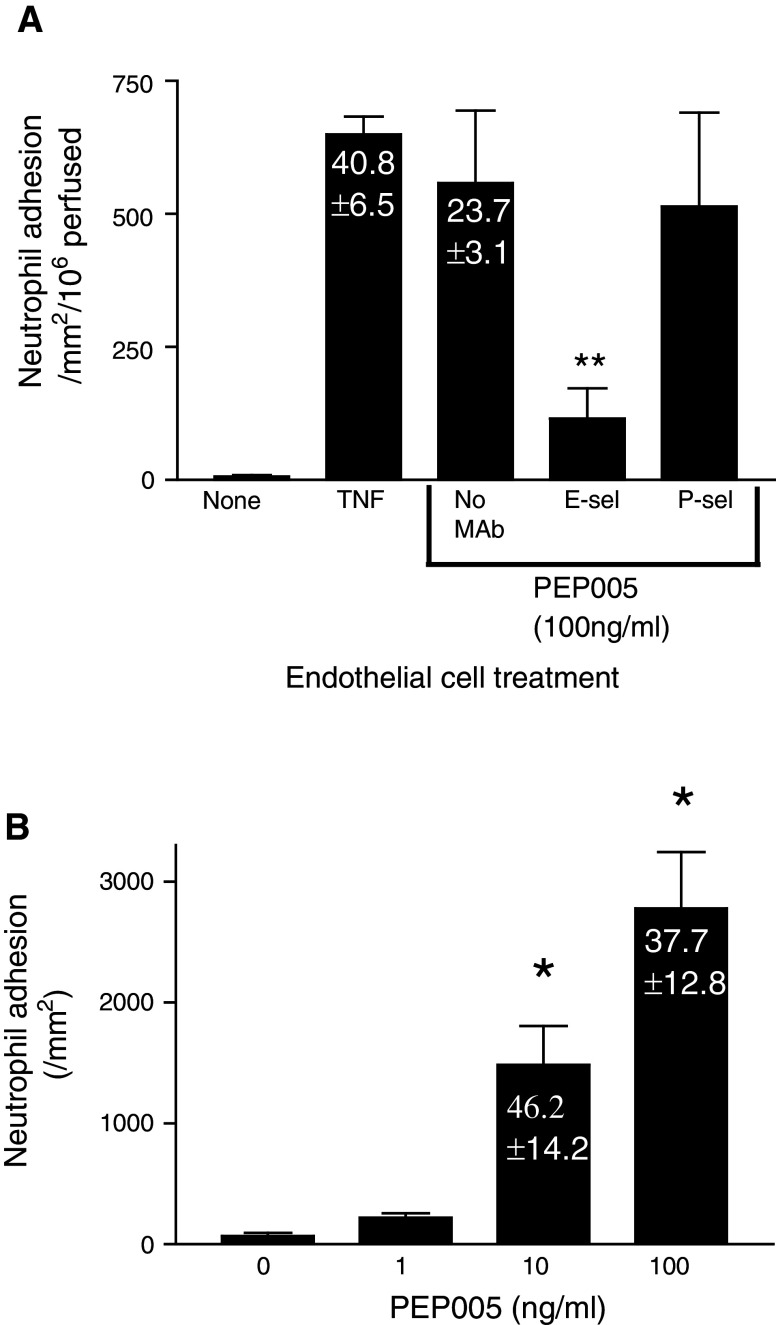
Fig. 1.
PEP005 activates EC so that they support the adhesion of flowing neutrophils in an E-selectin dependent manner. a EC monolayers treated for 4 h with TNF-α or PEP005 were subject to flow based adhesion assay. Both agents induced high levels of neutrophil adhesion with a substantial proportion of recruited cells going on to transmigrate into the sub-endothelial environment (% migrated cells inset into relevant bars). The adhesion of neutrophils to PEP005 stimulated EC was significantly inhibited by an antibody against E-selectin where as an anti-P-selectin antibody had no consistent effect on adhesion. Data are mean ± SEM of three experiments; **P < 0.01 by t test for comparison between PEP005 treated cells in the presence or absence of antibody. b The adhesion of neutrophils to microvascular EC monolayers stimulated with PEP005 in the range of 1–100 ng/ml. Neutrophil adhesion increased in a dose dependent manner and a substantial proportion of adherent cells migrated across the EC monolayer (% migrated cells inset into relevant bars). Data are mean ± SEM of three experiments; *P < 0.05 by t test for comparison between PEP005 treated and untreated cells