Figure 3: Combining pathogen detection and AMR gene profiling of mNGS and WGS data to investigate Klebsiella pneumoniae transfusion-related sepsis.
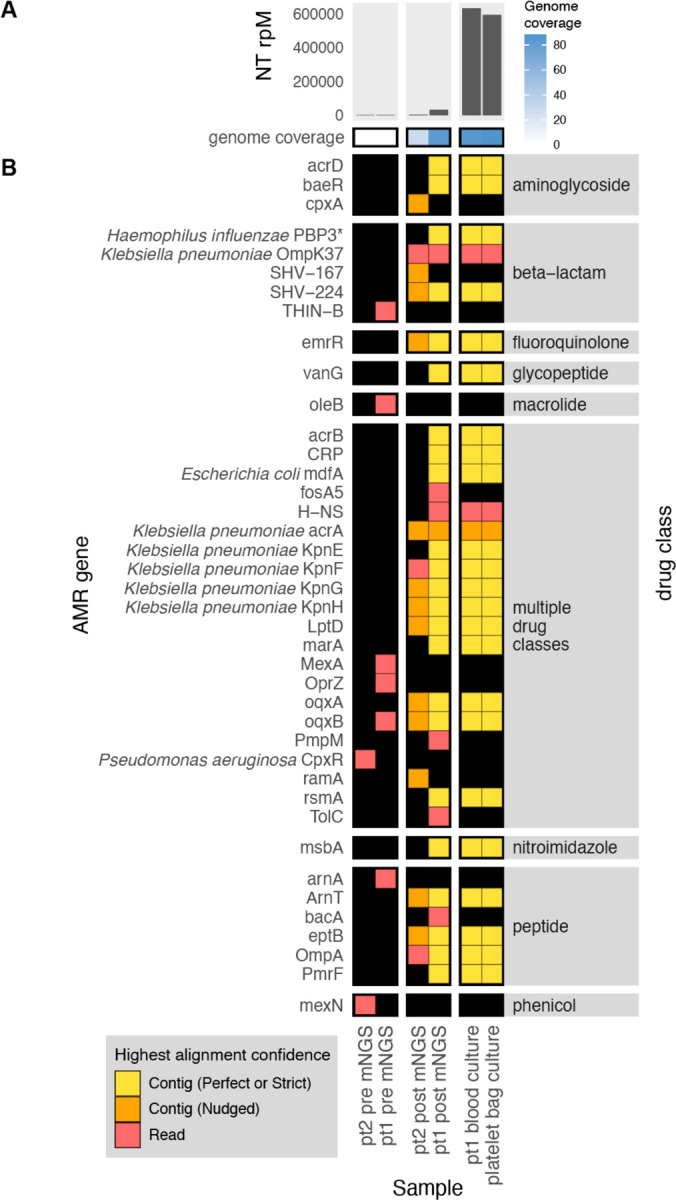
(A) Abundance and genome coverage of Klebsiella pneumoniae from direct mNGS of plasma or serum samples versus WGS of cultured bacterial isolates. (B) AMR genes detected in each sample. *denotes AMR gene(s) for which resistance originates due to point mutations (as opposed to presence/absence of the gene); these were detected by the “protein variant model” in CARD and the gene name shown is a representative reference gene containing the mutations known to lead to resistance. Legend: NT rPM = reads mapping to pathogen in the NCBI NT database per million reads sequenced. Contig = contiguous sequence. Strict/Perfect/Nudged refers to RGI’s alignment stringency threshold. “pt1” = patient 1, “pt2” = patient 2. “pre” = pre-transfusion, “post” = post-transfusion.
