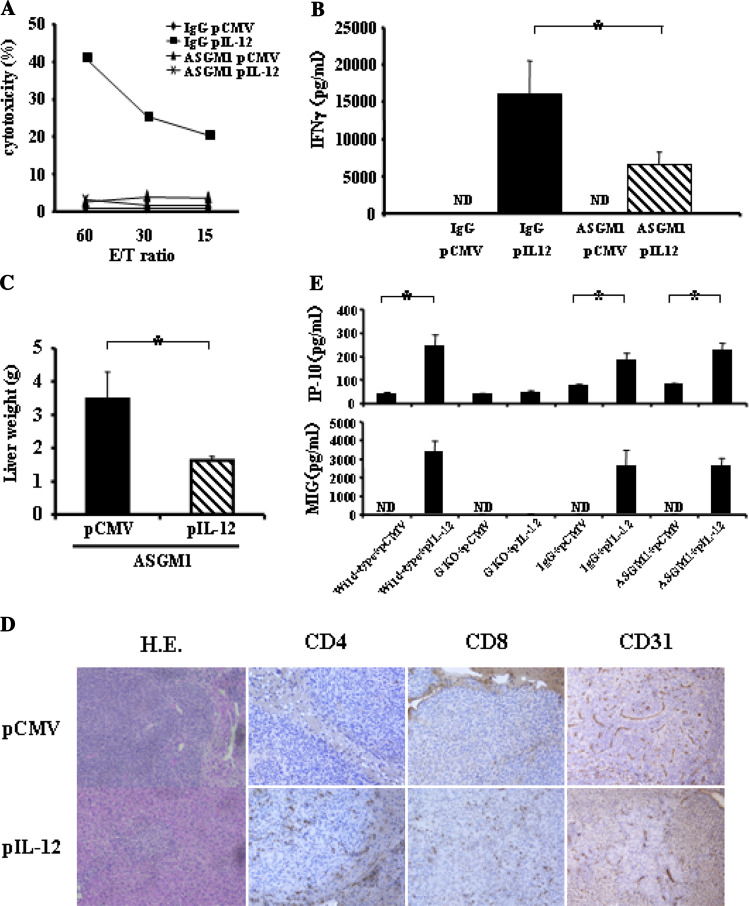
Fig. 6.
Anti-tumor effects of IL-12 in NK-cell-depleted mice. Serum IFNγ levels and NK-cell activation. Wild-type mice were intraperitoneally injected with either anti-asialoGM1 antibody (ASGM1) or control IgG, and, 1 day later hydrodynamically injected with either pCMV-IL-12 or pCMV. Mice were killed 4 days after plasmid injection. a Yac1 lytic ability of hepatic mononuclear cells is expressed as the indicated effector and target ratios (E/T ratio). Experiments were done 2 times and representative data are shown. b The levels of serum IFNγ are expressed as mean and SD (n = 6/ group). ND not detectable. *p < 0.005. Anti-metastatic effects. Wild-type mice were intrasplenically injected with CT-26 cells and, 1 day later and then every 5 days, intraperitoneally injected with either anti-asialoGM1 antibody (ASGM1) or control IgG, and hydrodynamically injected with either pCMV-IL-12 or pCMV 2 days after CT-26 injection. Fourteen days after plasmid injection, mice were killed to examine liver tumor development by measuring liver weight. c The results are indicated as mean and SD (n = 6/group). *p < 0.001. d Representative histology of liver sections analyzed by hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistochemistry of CD4, CD8 and CD31. e Serum levels of IP-10 and MIG. Wild-type or GKO mice were hydrodynamically injected with either pCMV-IL-12 or pCMV. Wild-type mice were intraperitoneally injected with either anti-asialoGM1 antibody (ASGM1) or control IgG, and 1 day later hydrodynamically injected with either pCMV-IL-12 or pCMV. Four days later, each mice were bled to measure the levels of serum IP-10 and MIG. Results are expressed as mean and SD (n = 6/group). ND not detectable. *p < 0.001