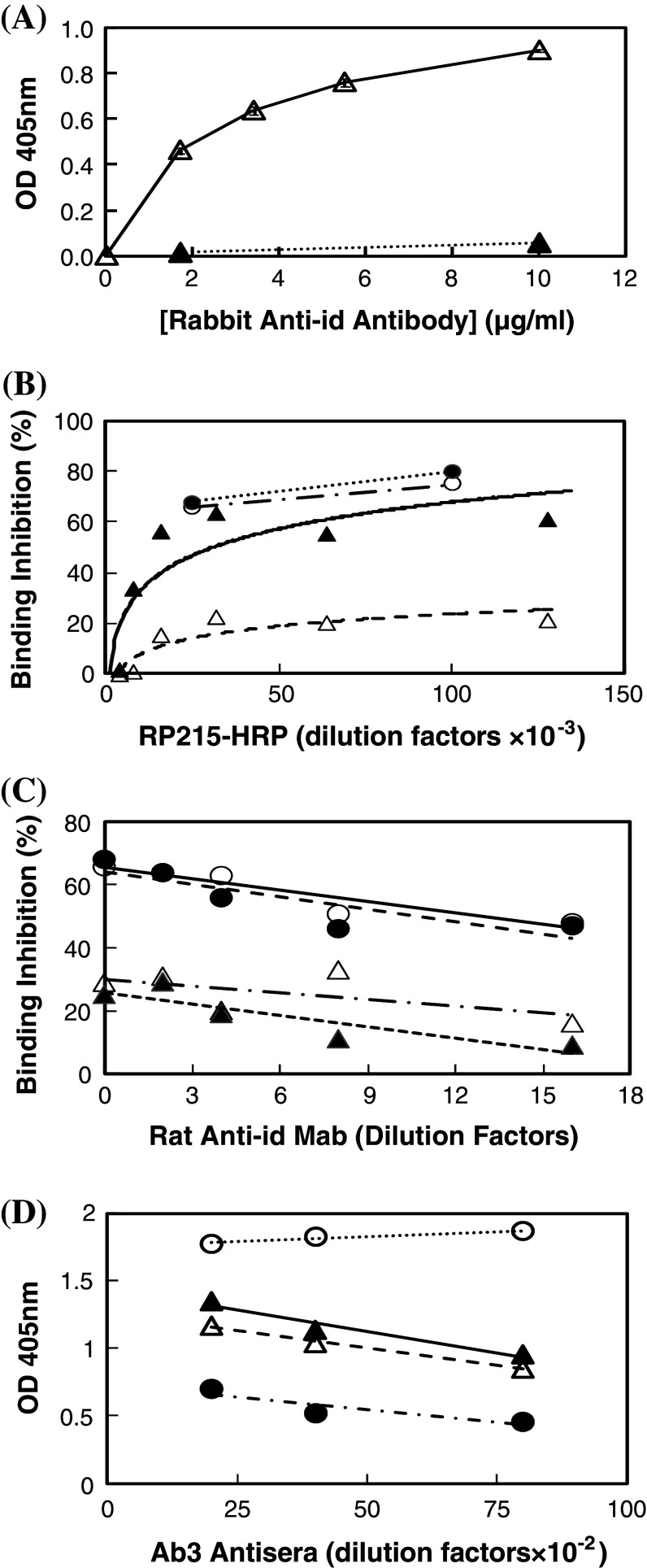
Fig. 1.
a ELISA to reveal the specificity of rabbit anti-id antibodies of RP215. Open triangles binding to RP215-coated microwells with alkaline phosphatase-labeled goat anti-rabbit IgG used as the secondary antibodies; filled triangles binding to normal mouse IgG-coated microwells. b ELISA with microwells coated with purified CA215 to reveal the presence of mouse or rat anti-id sera or Mabs of RP215 through the competitive binding between RP215-HRP of different dilutions and mouse anti-RP215 serum specimens at 1:100 dilutions as well as rat anti-RP215 Mabs (cell culture supernatants). Percentages of binding inhibition to wells coated with CA215 are plotted against RP215-HRP of different dilutions (initial concentration: ~1 mg/ml). Open triangles mouse anti-id sera #I; filled triangles mouse anti-id sera #R; open circles rat anti-id Mab #3; and filled circles rat anti-id Mab #11. c Inhibition of RP215-HRP (1:25,000 dilution from the initial concentration of ~1 mg/ml) binding to CA215 coated on microwells by rat anti-id Mabs from open circles rat anti-id Mab # 3; filled circles rat anti-id Mab #11; open triangles rat anti-id Mab #4; and filled triangles rat anti-id Mab #14 in cell culture supernatants of different dilutions. d ELISA to reveal the binding of mouse anti-anti-id sera at different dilutions to microwells coated with CA215 and compared with that of RP215 (initial concentration: 1 mg/ml). Normal mouse serum was used as the negative control. Open triangles mouse #I; open circles mouse #L; filled triangles mouse #R; filled circles purified RP215 (initial concentration: 1 mg/ml). Data presented are averages of duplicated experiments