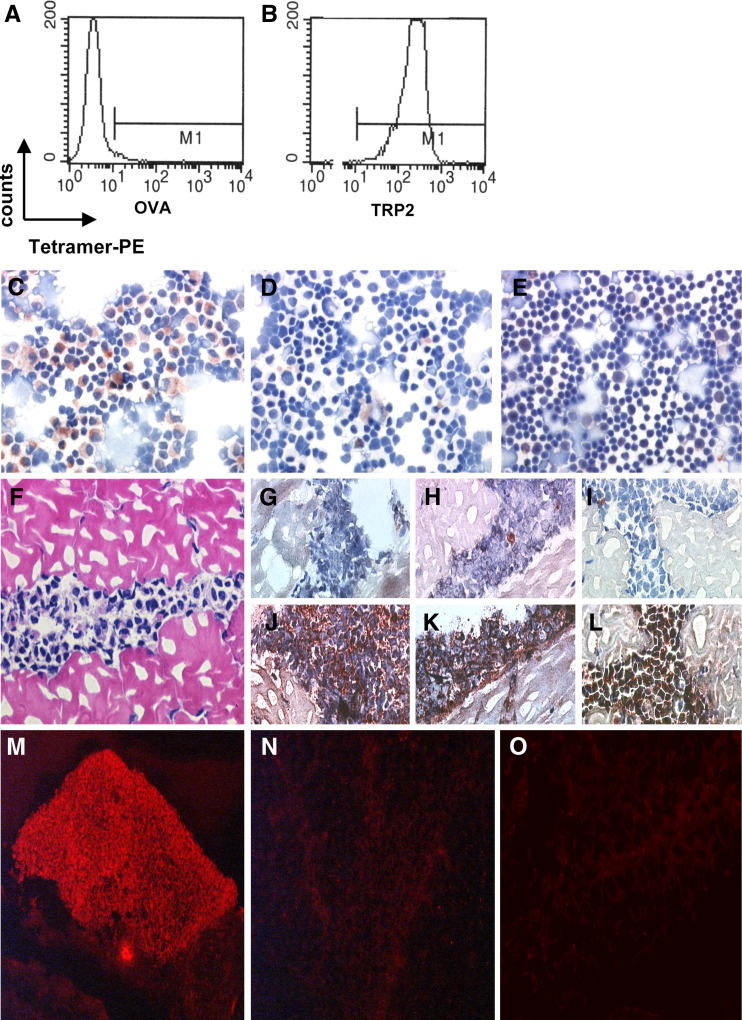
Fig. 1.
In situ detection of antigen-specific T cells. Flow cytometric analysis of tetramer binding by LP9 T cells, control tetramer H-2Kb-OVA (a) and relevant tetramer H-2Kb-TRP2180 (b). Positive staining of a cytological preparation containing LP9 cells and normal C57BL splenocytes was only observed with H-2Kb-TRP2180 tetramer (c) and not without tetramer (negative control) (d). Staining of normal splenocytes with H-2Kb-TRP2180 tetramer did not result in a positive signal (e). H&E-stained section of LP9-containing muscle tissue (f). Improved morphology and signal to noise ratios of in situ detection of antigen specific T cells in LP9-containing muscle tissue sections stained histochemically with specific tetramers (j–l) or negative control solution (without tetramer) (g–i) using the ABC-peroxidase kit with AEC (red-brown staining) as substrate. g, j Without blocking with normal goat serum and PFA-fixation prior to staining. h, k With normal goat serum blocking but without PFA-fixation prior to staining. i, l With blocking with normal goat serum and PFA-fixation prior to staining. LP9-containing muscle tissue sections stained with or without tetramers with fluorescent microscopy visualization. Positive staining was observed after incubation with specific H-2Kb-TRP2180 tetramers (m) and not without the addition of tetramer (n) or after incubation with control tetramer H-2Kb-OVA