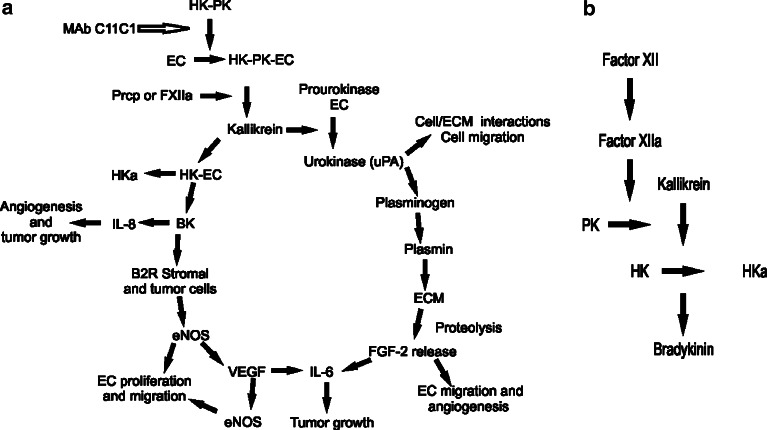
Fig. 6.
The Plasma Kallikrein–Kinin System and mAb C11C1 effect in the angiogenic cascade. a C11C1 mAb and the angiogenic cascade. MAb C11C1 C11C1 monoclonal antibody. HK high-molecular-weight kininogen. PK prekallikrein. EC endothelial cell. Prcp prolylcarboxypeptidase. FXIIa activated coagulation factor XII. HKa cleaved high-molecular-weight kininogen. IL-8 interleukin 8. BK bradykinin. B2R bradykinin 2 receptor. eNOS endothelial cell nitric oxide system. VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor. IL-6 interleukin 6. FGF-2 fibroblast growth factor 2, basic fibroblast growth factor. ECM extracellular matrix. uPA urokinase type plasminogen activator. The plasma complex HK–PK binds to the endothelial cells, where PK is activated to kallikrein (by either Prcp or FXIIa). Kallikrein cleaves HK releasing HKa and BK. BK stimulates IL-8 secretion (a potent angiogenic and tumor growth inducer) and the production and secretion of eNOS through the B2R on the surface of stromal and tumor cells. eNOS induces endothelial cell release of VEGF and endothelial cell proliferation and migration. VEGF induces eNOS and IL-6 release (which promotes tumor growth). Kallikrein also cleaves prourokinase to urokinase initiating a different pathway. Urokinase is involved in cell/ECM interactions favoring tumor spread and endothelial cell migration. Urokinase also activates plasminogen into plasmin and the proteolysis of the extracellular matrix releasing FGF-2. FGF-2 induces endothelial cell migration and the release of IL-6, which promotes tumor growth. MAb C11C1 inhibits the adhesion of HK and/ or the HK–PK complex to the endothelial cells, inhibiting the BK and uPA activation through kallikrein thus inhibiting tumor angiogenesis and growth. b Plasma Kallikrein-Kinin system: Consists of three proteins, Factor XII (FXII), Prekallikrein (PK), and high-molecular-weight kininogen (HK). Activated FXII (FXIIa) cleaves PK to kallikrein; kallikrein cleaves HK releasing BK and activated HK (HKa)