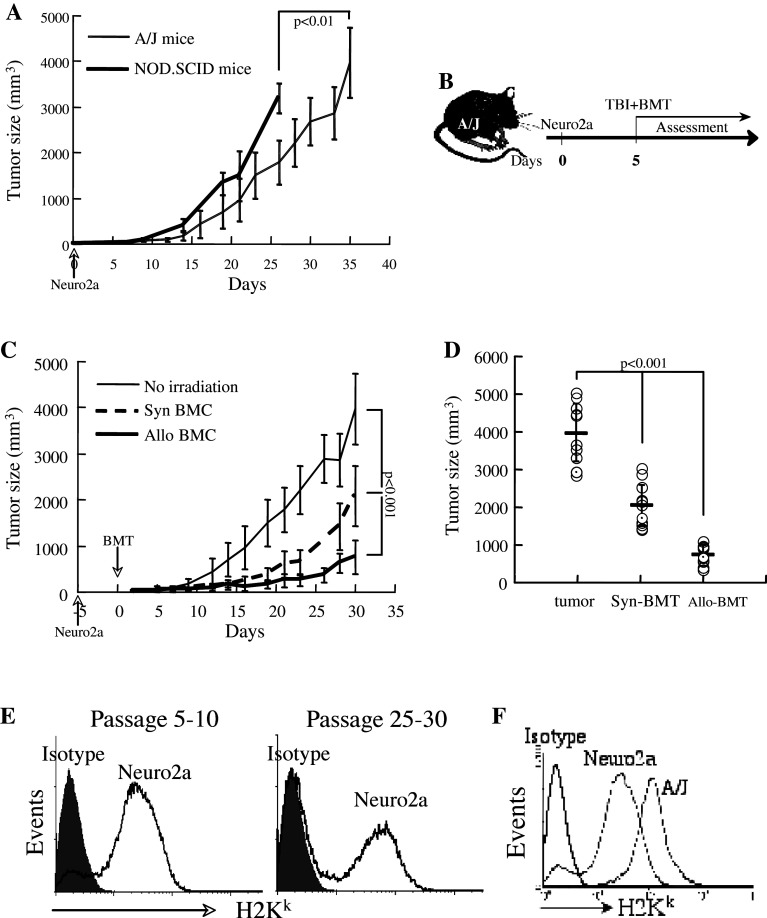
Fig. 1.
Neuro-2a growth is affected by T cell immunity. a 106 Neuro-2a cells were injected subcutaneously into congenic H2Ka (n = 15) and immunocompromized NOD.SCID mice (n = 8). Tumor volume was evaluated according to: length × width2 × 0.4, until the tumors reached maximal allowed sizes. Data represent means ± standard deviations (SD). b The time sequence for transplant experiments: total body irradiation at 700 rad and intravenous infusion of bone marrow cells were performed 5 days after subcutaneous implantation of 106 Neuro-2a cells. c Transplantation of 5 × 106 syngeneic (n = 11) and allogeneic (n = 19) whole bone marrow cells (BMC) resulted in reduced growth rate of the tumors. Data represent means ± SD. d Tumor size at 30 days after syngeneic (H2Ka → H2Ka) and allogeneic (H2 Kb → H2Ka) bone marrow transplantation as compared to growth in naïve congenic (H2Ka) mice. e Expression of H2Ka antigen in Neuro-2a cells using a cross-reactive anti-H2Kk antibody: left panel passage 6, right panel passage 25. f Low level expression of H2Kk in Neuro-2a cells as compared to splenocytes of A/J mice