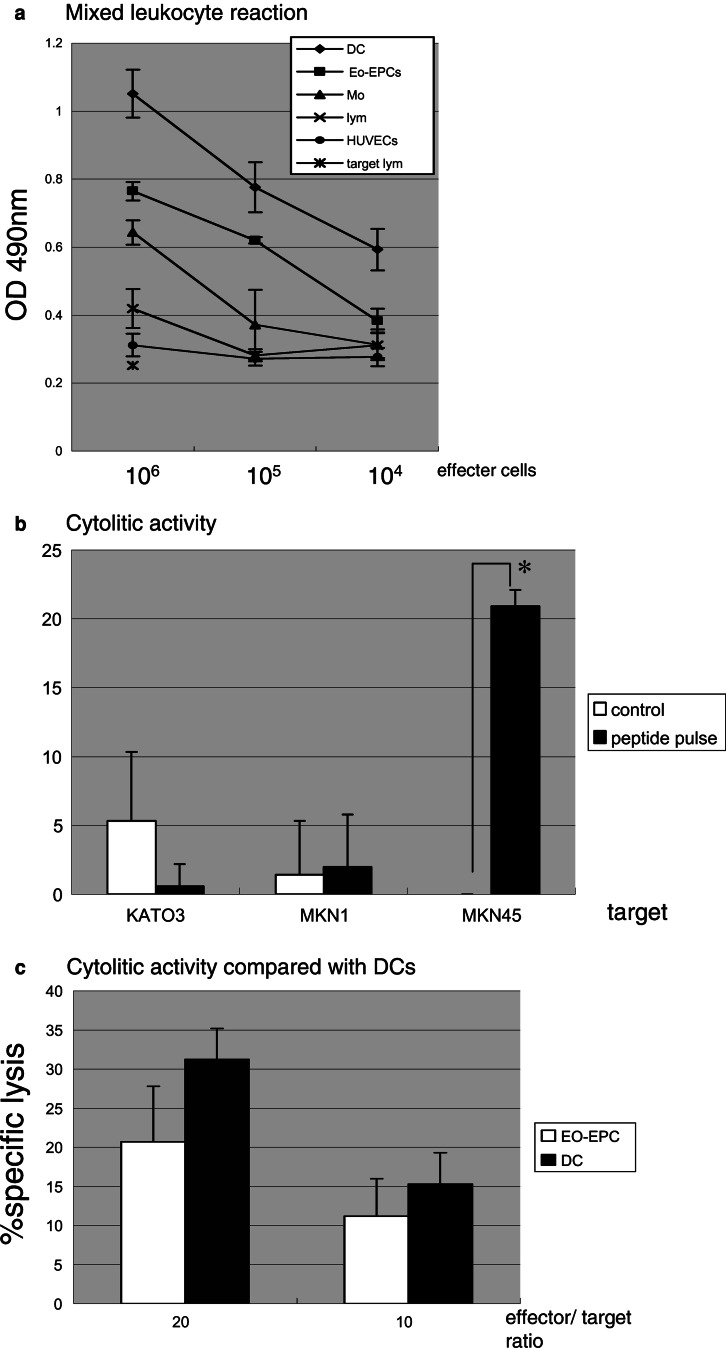
Fig. 6.
a The effect of EO-EPCs to stimulate the proliferation of allogeneic lymphocytes. EO-EPCs effectively stimulated the proliferation of allogeneic lymphocytes, but compared to DCs, the effect was weaker. b EO-EPCs were tested for their ability to stimulate HLA-restricted, CEA-specific autologous CTLs, and their ability to lyze tumor cells in vitro. CTL generated by co-culture with CEA peptide-pulsed EO-EPCs specifically and effectively lyzed the HLA-A24+, CEA+ gastric cancer cells, but not the HLA-A24(−) and/or CEA(−) cells. *P<0.05 (c) Comparison between CTLs generated by EO-EPCs and those generated by DCs, related to the lytic activity against gastric cancer cells. Both EO-EPCs and DCs were pulsed with HLA-A24-restricted CEA peptide, and then co-cultured with autologous lymphocytes. Cytotoxity of EO-EPCs-induced CTLs was weaker than that induced by DCs