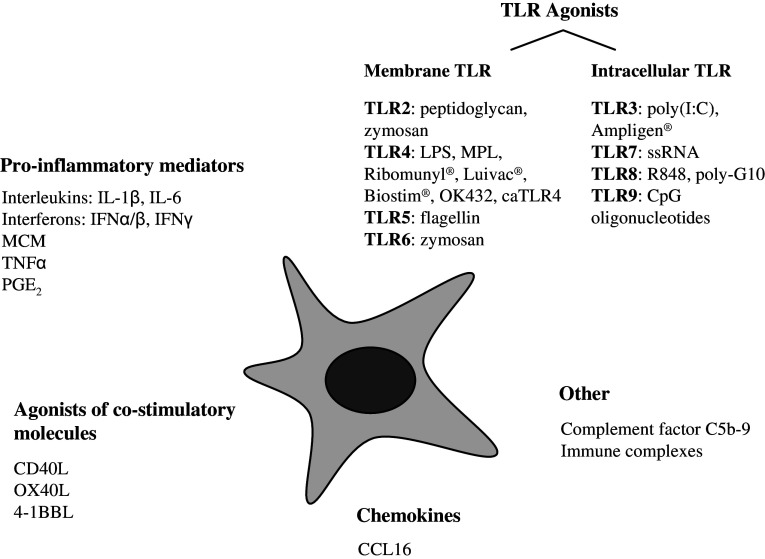
Fig. 2.
Schematic representation of the currently available maturation stimuli. To date, several stimuli have been identified which promote DC maturation. The extent to which DC maturation is affected varies considerably between individual stimuli. In addition, it has been shown that distinct combinations of maturation stimuli can act synergistically to promote DC maturation and Th1 polarizing capacity of DC. Ongoing research will possibly identify optimal combinations of stimuli for DC maturation. Although clinical-grade bacterial immunomodulators (Ribomunyl®, Luivac®, Biostim®, OK432) are classified in this figure as TLR4 agonists, the nature of these stimuli suggests that they possibly trigger a combination of distinct TLR. Agonists of co-stimulatory molecules can be delivered by agonistic Ab, soluble ligands (if available) and transfection with ligands. MCM monocyte-conditioned medium, MPL monophosphoryl lipid A, caTLR4 constitutively active TLR4