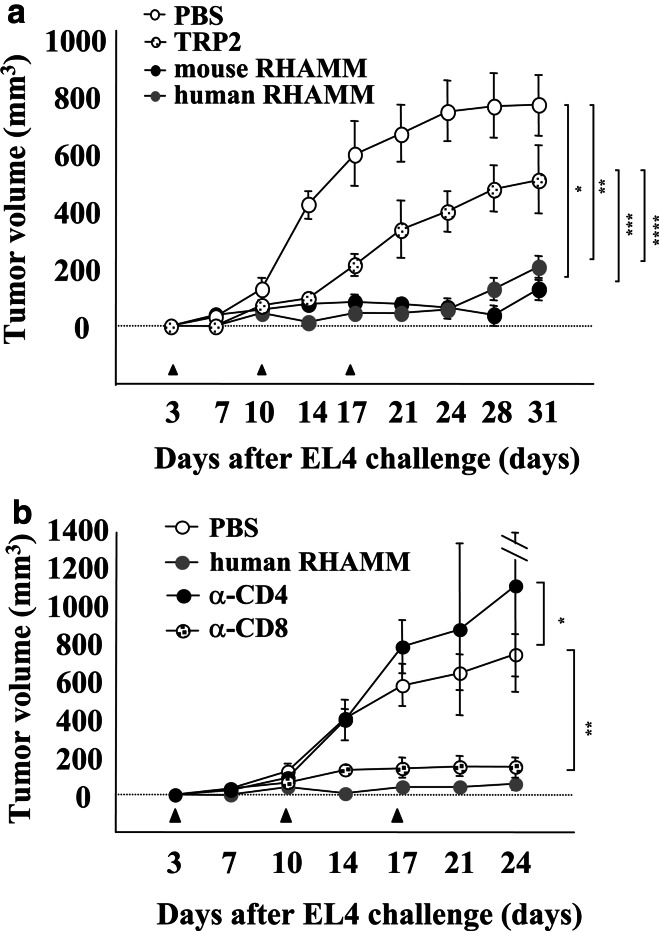
Fig. 5.
Treatment of tumor-bearing mice with RHAMM mRNA-transfected DCs. a 3×105 EL4 cells were inoculated subcutaneously into the right flank of C57BL/6 mice. After 3, 10 and 17 days, 3×105 DC/PBS, DC/TRP-2, DC/mRHAMM or DC/hRHAMM were injected subcutaneously in the vicinity of the tumor inoculation site of mice. Tumor sizes were measured biweekly. A two-tailed Student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance of differences in tumor growth among the treatment groups. *DC/PBS versus DC/mRHAMM (P<0.0001); **DC/PBS versus DC/hRHAMM (P<0.0001); ***DC/TRP2 versus DC/mRHAMM (P=0.0013); ****DC/TRP2 versus DC/hRHAMM (P=0.0008). b Effect of CD4+ or CD8+ T cell depletion on the efficacy of DC/RHAMM treatment. Mice were treated with an anti-CD4 or anti-CD8 antibody at 3 days before the tumor challenge, followed by two injections per week. 3×105 EL4 cells were inoculated subcutaneously into the right flank of the mice. After 3, 10 and 17 days, 3×105 DC/PBS or DC/hRHAMM were injected subcutaneously in the vicinity of the tumor inoculation site of mice. Tumor sizes were measured biweekly. A two-tailed Student’s t test was used to determine the statistical significance of differences in tumor growth among the treatment groups. *DC/PBS versus DC/hRHAMM + anti-CD4 (P=0.1177); **DC/PBS versus DC/hRHAMM + anti-CD8 (P=0.0006)