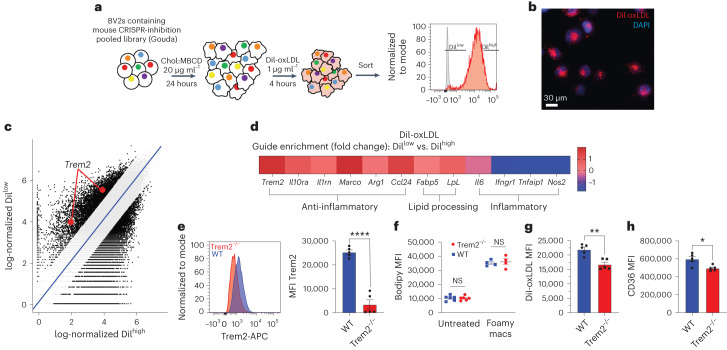
Fig. 2. Genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies Trem2 as a candidate regulator for foamy macrophage formation.
a, Schematic for CRISPR knockout screening approach for oxLDL uptake. BV2 macrophages were loaded with CRISPR pooled guide library (Gouda). Cells were made foamy by overnight treatment with soluble cholesterol and then challenged for 4 h with DiI-oxLDL and sorted for DiIhigh and DiIlow cells. Guides were sequenced from sorted populations. b, Confocal micrograph showing BV2 DiI uptake after 4-h incubation with DiI-oxLDL. Representative of two independent experiments. c, CRISPR guide enrichment comparing log-normalized enrichment in DiIhigh (x axis) versus DiIlow (y axis). Gray error bands delineate guides with log fold change < 1. d, Selected gene enrichments comparing DiIlow versus DiIhigh. e, Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT or Trem2−/− mice and treated with soluble cholesterol to induce foamy cell formation. After overnight culture, cells were analyzed for Trem2 expression by flow cytometry (n = 5 biologically independent replicates per group). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test, ****P < 0.0001. f, Bodipy staining for total neutral lipid accumulation was performed by flow cytometry on peritoneal macrophages from WT or Trem2−/− mice, cultured overnight in media alone or in media with soluble cholesterol (n = 6 biologically independent replicates for untreated and n = 4 biologically independent replicates for foamy). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test. g, Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT or Trem2−/− mice and treated with soluble cholesterol to induce foamy cell formation. After overnight culture, cells were treated with DiI-oxLDL for 4 h and assessed for uptake by flow cytometry (n = 5 biological replicates per group). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test, **P < 0.01. h, CD36 expression from peritoneal macrophages isolated from WT or Trem2−/− mice and treated with soluble cholesterol overnight to induce foamy cell formation (n = 5 biological replicates per group). Data are mean ± s.e.m. Student’s t-test, *P < 0.05. NS, not significant.