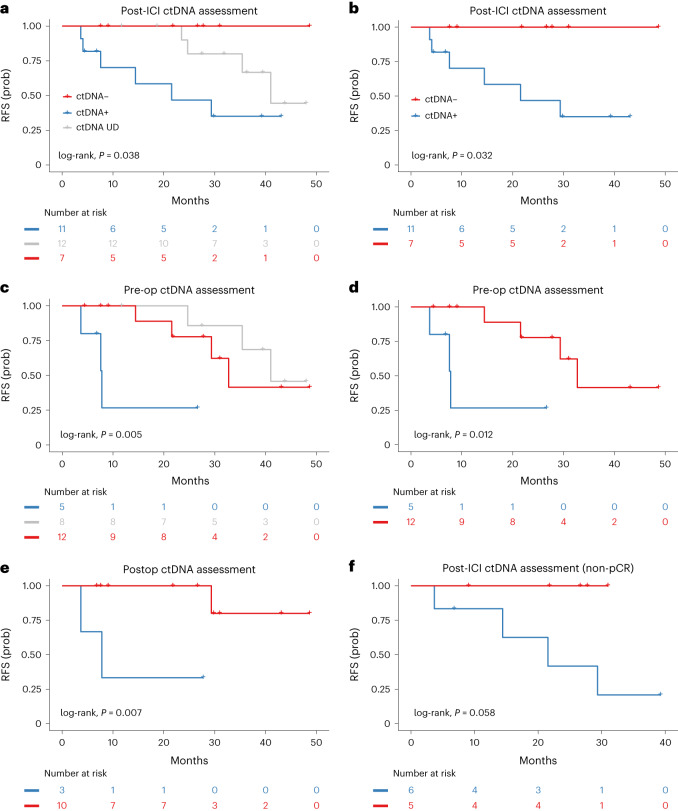
Fig. 4. Association of ctDNA assessment and RFS.
ctDNA detection was assessed at the post-ICI, preoperative and postoperative timepoints. a, Patients with undetectable DNA throughout the study (gray) or undetectable ctDNA post-ICI (red) had a longer RFS compared to patients with detectable ctDNA (blue) post-ICI (median RFS 41.02 months versus not reached versus 21.54 months, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.038). b, Patients with undetectable ctDNA at the post-ICI time point had a longer RFS compared to patients with detectable ctDNA post-ICI (median RFS not reached versus 21.54 months, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.032). c,d, Patients with undetectable ctDNA throughout the study or at the preoperative time point had a longer RFS compared to patients that had detectable ctDNA at the preoperative time point (median RFS 41.02 versus 32.72 versus 7.80 months, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.005 (c), and median RFS 32.72 versus 7.80 months, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.012 (d)). e, Patients with undetectable ctDNA at the postoperative time point had a longer RFS compared to patients with detectable ctDNA (median RFS not reached versus 7.80 months, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.007). f, When ctDNA was assessed among patients who did not attain a pCR, non-pCR patients with undetectable ctDNA post-ICI had a longer RFS compared to non-pCR patients with detectable ctDNA post-ICI (median RFS not reached versus 21.54, respectively; log-rank, P = 0.058).