Figure 2. Preferred Route of Vasopressor Initiation Among Respondents Who Chose to Start Vasopressors.
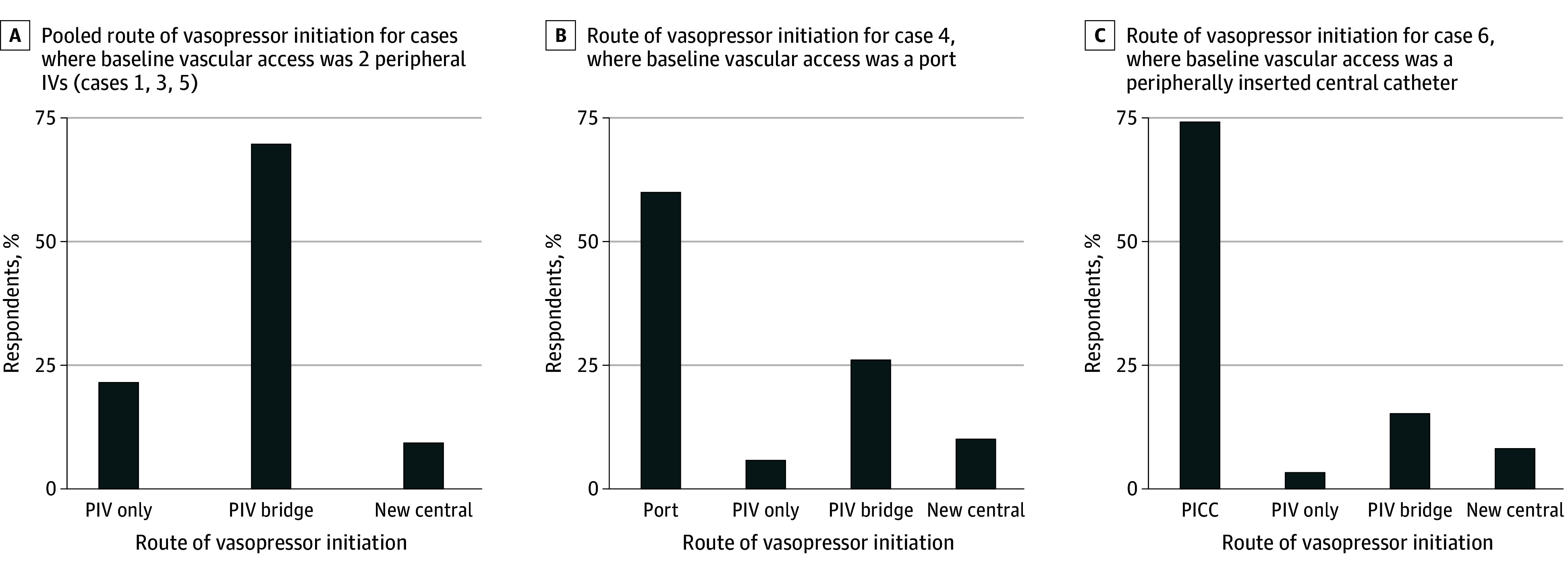
The figure shows the pooled route of vasopressor initiation for cases 1, 3, and 5, where baseline vascular access was 2 PIVs (A; based on 1127 vignettes), the route of vasopressor initiation for case 4, where baseline vascular access was a port (B; based on 390 vignettes), and the route of vasopressor initiation for case 6, where baseline vascular access was a PICC (C; based on 367 vignettes). Case 2 was not included in this analysis because the patient in case 2 had a preexisting new temporary central line, which was presumed to be the default route of vasopressor initiation. PICC indicates peripherally inserted central catheter; PIV, peripheral venous catheter. PIV only refers to starting the vasopressor peripherally; PIV bridge refers to starting the vasopressor peripherally but planning to place a new central line; and new central refers to placing a new central line before starting the vasopressor.
