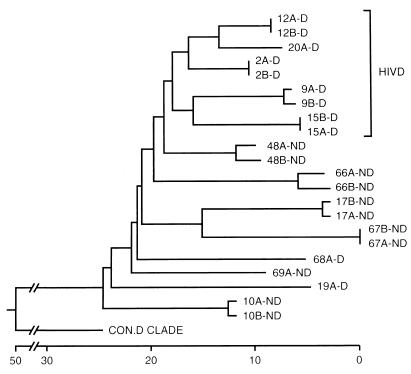
FIG. 2.
Phylogenetic comparison of brain-derived V1-V2 sequences obtained from HIV-D (D) and HIV-ND (ND) individuals with AIDS and the consensus sequence from clade D (con.D clade) (38), using neighbor-joining analysis (30). Numbers refer to individual patients, and letters (A and B) refer to clones from the same patient. Two clones were analyzed for each patient. Clones from five of seven HIV-D patients clustered together, while none of the HIV-ND patients showed close associations. The horizontal axis represents the number of substitution events. Analysis of the V1 and V2 sequences separately revealed no clustering of sequences from the same clinical group. Similar topologies were obtained with different phylogenetic methods, but bootstrap values were low (<70) between individuals.