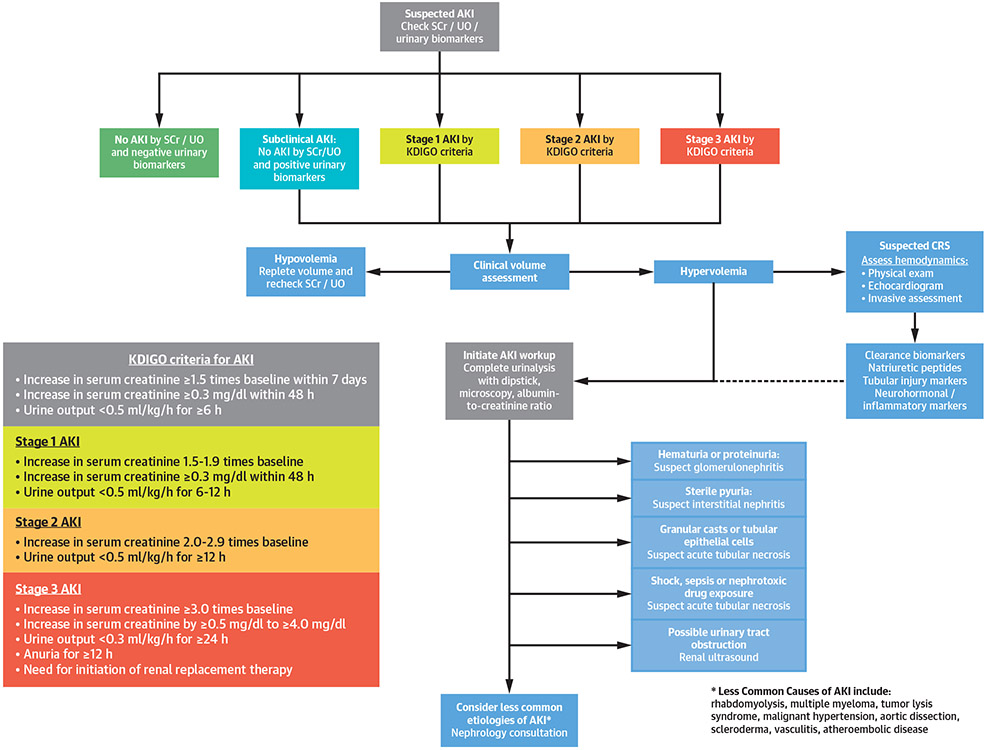
FIGURE 2. Diagnostic Approach to Patients With Suspected AKI.
AKI is defined as an acute reduction in urine output or increase in serum creatinine level and is divided into 3 Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) AKI stages of increasing severity (21,30). The diagnostic approach for patients with AKI includes assessment of volume status and focused testing to exclude potential etiologies, including biomarker testing (21,30,32,34). Natriuretic peptides include B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP) and N-terminal pro-BNP (NT-proBNP). Urinary biomarkers include TIMP-2 and IGFBP-7. Clearance biomarkers include serum creatinine (SCr), blood urea nitrogen (BUN), and cystatin C. Tubular injury biomarkers include KIM-1, L-FABP, and NGAL. Neurohormonal and/or inflammatory biomarkers include growth differentiation factor (GDF)-15, ST-2, and cancer antigen 125 (CA-125). UO = urinary output; other abbreviations as in Figure 1.