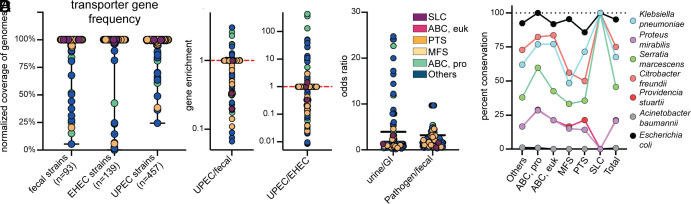
Fig. 1.
Diverse uropathogens display high conservation of ABC transporters. (A) All 640 KEGG-annotated transporter protein products in UPEC strains CFT073 were surveyed for homology against fecal (n = 93), enterohemorrhagic (n = 139), and uropathogenic (n = 457) isolates of E. coli, with a protein identity and coverage over 90% defining a hit. Each dot represents a single protein from strain CFT073 and indicates the relative number of strains it was detected in within each cohort, using an amino acid cutoff of >90%. These are color-coded based on the family of transporters: solute carrier (purple), ABC eukaryotic-like (pink), phosphotransferase (orange), major facilitator superfamily (yellow), ABC prokaryotic-like (green), and Others (blue). (B) An enrichment analysis was performed comparing each transporter in UPEC relative to either fecal or EHEC isolates. A value greater than 1 indicates an enrichment in UPEC genomes, and <1 indicates enrichment in fecal or EHEC genomes. The dashed red line indicated the median of these data. (C) Based on the prevalence determined, an odds ratio was calculated for each transport protein. The odds ratios in strains isolated from human urine compared to the gastrointestinal tract (GI, both fecal and EHEC) and pathogenic isolates (UPEC and EHEC) compared to commensal fecal isolates. (D) All E. coli CFT073 KEGG-annotated transporters were surveyed against the pathogenic type strains (uropathogenic or bacteremic) of six different bacterial species, in addition to the commonly used UPEC isolate UTI89. Dots indicate the percent conservation of each transport system in every species, displayed by family.