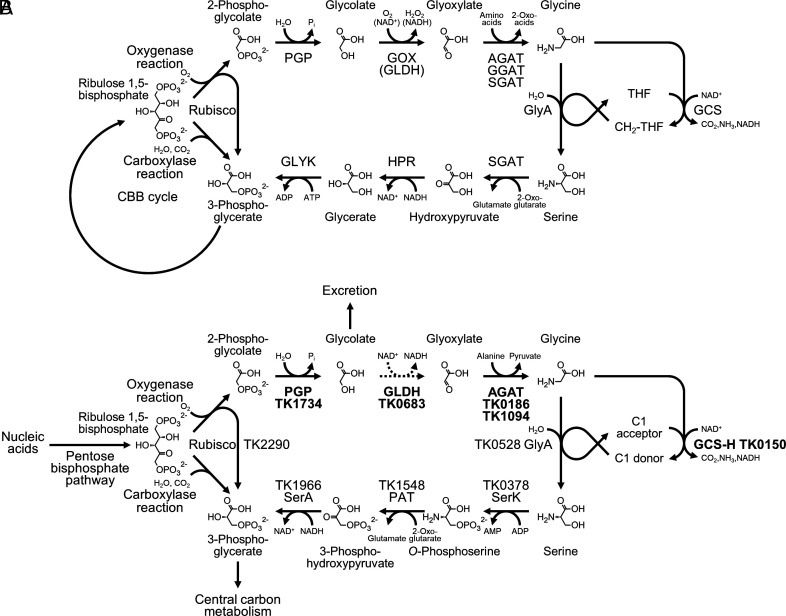
Fig. 1.
The classical C2 pathway and 2-PG removal in Thermococcus kodakarensis. (A) The classical photorespiration pathways in plants, algae, and cyanobacteria consist of 2-PG phosphatase (PGP), GOX or glycolate dehydrogenase (GLDH), alanine:glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGAT), glutamate:glyoxylate aminotransferase (GGAT) and/or serine:glyoxylate aminotransferase (SGAT), serine hydroxymethyltransferase (GlyA), glycine cleavage system (GCS), serine:2-oxoglutarate aminotransferase or SGAT, hydroxypyruvate reductase (HPR), and GLYK. (B) 2-PG removal/salvage proposed in T. kodakarensis. Dephosphorylation of 2-PG and excretion of glycolate have been experimentally verified. GLDH that catalyzes the oxidation of glycolate is not a homolog of previously identified GLDH enzymes, and is a member of the lactate dehydrogenase family. Activity levels of GLDH in T. kodakarensis cells are much lower than those of other enzymes, and the conversion is thus indicated by a dotted arrow. The enzymes in a potential route from serine to 3-phosphoglycerate are serine kinase (SerK), phosphoserine aminotransferase (PAT), and 3-phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (SerA). Distinct to the classical C2 pathway, phosphorylation precedes transamination and reduction. Genes and proteins experimentally validated in this study are indicated in bold.