FIGURE 8.
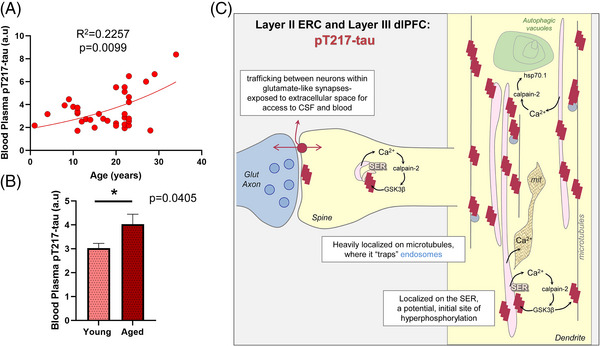
Increased pT217‐tau in blood plasma in aging rhesus macaques, and a working model of pT217‐tau etiology and toxic actions. Age‐related elevation in pT217‐tau in blood plasma in aging rhesus macaques (A). Results from a regression analysis performed in all animals (N = 36) indicated statistically significant increases in pT217‐tau signal with advancing age (R 2 = 0.2257, P = 0.0099). Quantification of pT217‐tau in blood plasma grouped by age (B). Young animals (N = 15) are compared to aged animals (N = 21) via a two‐tailed Welch t test (*P = 0.0405). SEM is plotted for each group. Summary schematic of pT217‐tau expression patterns in “early” aged (18–24 years) macaque ERC layer II and in “late” aged (26–31 years) macaque dlPFC layer III microcircuits (C). A schematic illustration of pT217‐tau localization in dendrites, and its potential etiology and toxic actions. pT217‐tau is primarily located in glutamatergic dendrites and dendritic spines, consistent with the known origins of tau pathology in dendrites in humans. 45 The current study found evidence of pT217‐tau trafficking between neurons at glutamate‐like synapses, interfacing with the extracellular space to become accessible in CSF and plasma. This may contribute to tau “seeding” pathology through an interconnected network of glutamatergic neurons. Aggregations of pT217‐tau were prominently expressed on microtubules, as well as on the calcium‐storing SER, where increased calcium release may drive GSK3β hyperphosphorylation of tau at T217. These dendrites often showed signs of pathology: autophagic vacuoles that are an early sign of autophagic degeneration and abnormal mitochondria (mit), known as MOAS. The aggregations of pT217‐tau on microtubules could be seen to “trap” endosomes, interfering with intracellular trafficking needed for healthy dendrites. These “endosomal traffic jams” may also increase the production of Aβ by increasing the time APP spends in endosomes with exposure to β‐secretase, a hypothesis to be tested in future research. Aβ, amyloid beta; APP, amyloid precursor protein; CSF, cerebrospinal fluid; dlPFC, dorsolateral prefrontal cortex; End, endosome; ERC, entorhinal cortex; Mit, mitochondria; MOAS, mitochondria on a string; pT217‐tau, tau phosphorylated at threonine‐217; SEM, standard error of the mean; SER, smooth endoplasmic reticulum
