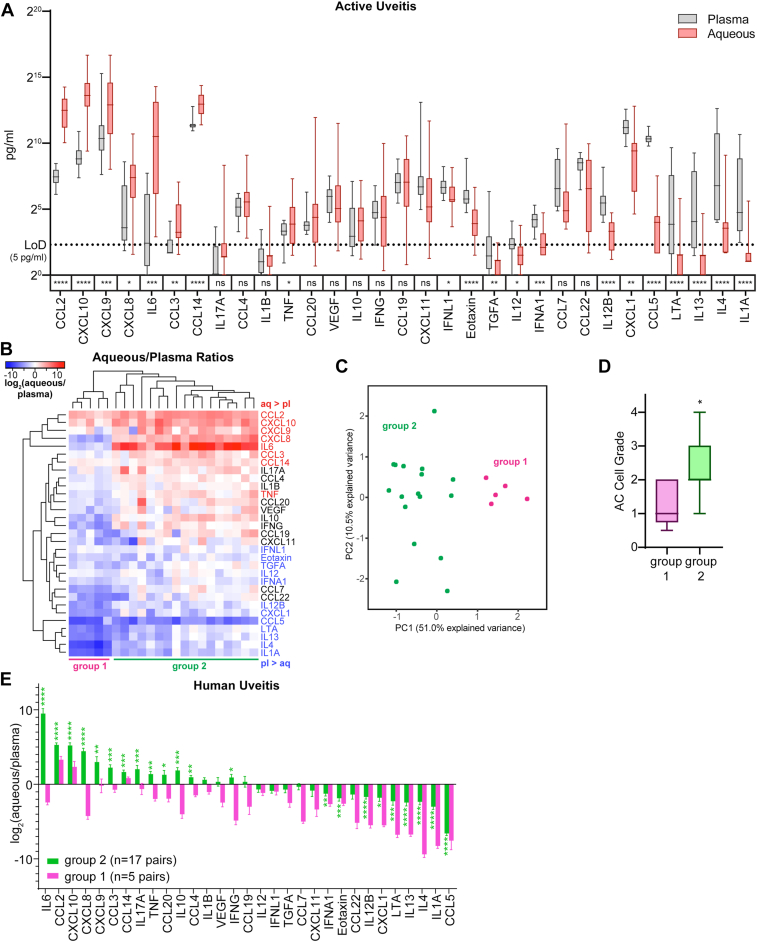
Figure 2.
CCL2 and CXCL10 are among the most aqueous-enriched proteins during active human uveitis. A, Paired measurements of chemokines and cytokines in aqueous fluid and plasma from n = 22 patients with active uveitis. We assessed for enrichment in either tissue using Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. The limit of detection (LoD) was protein- and assay-dependent but was approximately 5 pg/ml. Protein concentrations are plotted on a log scale. B, Heatmap showing the logarithmized ratios for each protein measured in aqueous to that measured in the plasma. Protein names are colored based on whether they were more abundant in aqueous than plasma (red) or more abundant in plasma than aqueous (blue). C, Principal component analysis plot of aqueous/plasma protein ratios. D, Comparison of anterior chamber cell grades between groups 1 and 2. Statistical significance was assessed using Mann–Whitney test. E, Aqueous-to-plasma protein ratios in our cohort of human uveitis patient separated by group. We assessed for enrichment in either tissue using Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test. Statistical significance is indicated as follows: ∗P < 0.05; ∗∗P < 0.01; ∗∗∗P < 0.001; and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001. AC = anterior chamber; CCL = C-C motif chemokine ligand; CXCL = C-X-C motif chemokine ligand; IFNA = interferon-alpha; IFNG = interferon-gamma; IFNL = interferon-lambda; IL = interleukin; LTA = lymphotoxin-alpha; TGFA = transforming growth factor-alpha; TNF = tumor necrosis factor.