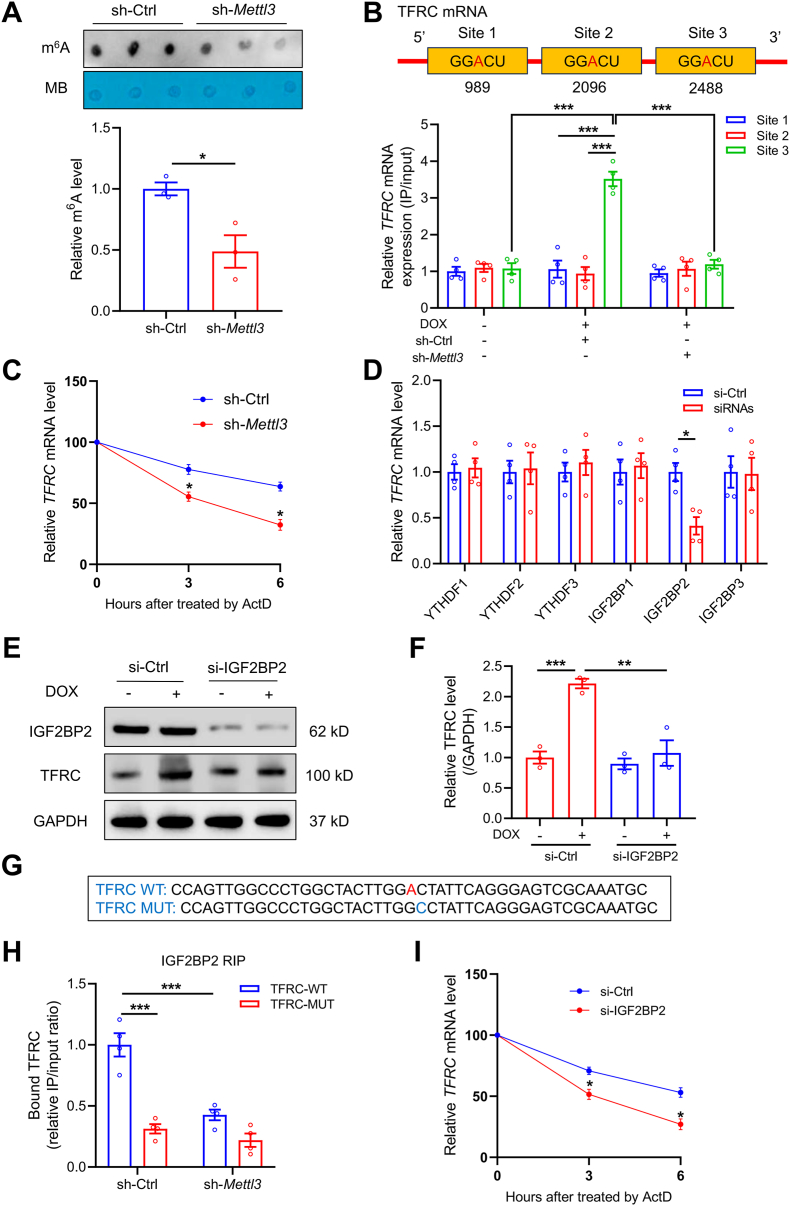
Fig. 7.
TFRC serves as a target for METTL3-mediated m6A modification via an IGF2BP2-dependent manner. (A) Representative m6A dot blot and statistical analysis of m6A with or without METTL3 knockdown (n = 3 per group). (B) MeRIP-qPCR analysis showing location of given m6A methylation sites in TFRC (n = 4 per group). (C) Decay rate of TFRC mRNA after treatment of actinomycin D (ActD, 5 μg/ml) in METTL3 knockdown HL-1 cells (n = 3 per group). (D) Relative mRNA levels of TFRC in HL-1 cells knocked down with YTH and IGF2BP reader proteins (n = 4 per group). (E) and (F) Relative protein level of TFRC in the absence or presence of IGF2BP2 knockdown (n = 3 per group). (G) Sequences of TFRC RNA fragments with either WT or mutated (MUT) m6A sites. (H) RIP assay showing the binding affinity between TFRC mRNA and IGF2BP2 with or without METTL3 knockdown (n = 4 per group). (I) Decay rate of TFRC mRNA following ActD administration in IGF2BP2 knockdown HL-1 cells (n = 3 per group). Mean ± SEM. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's post-hoc test (F, and H) or unpaired two-tailed Student's t-test (A, C, D, and I). P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.