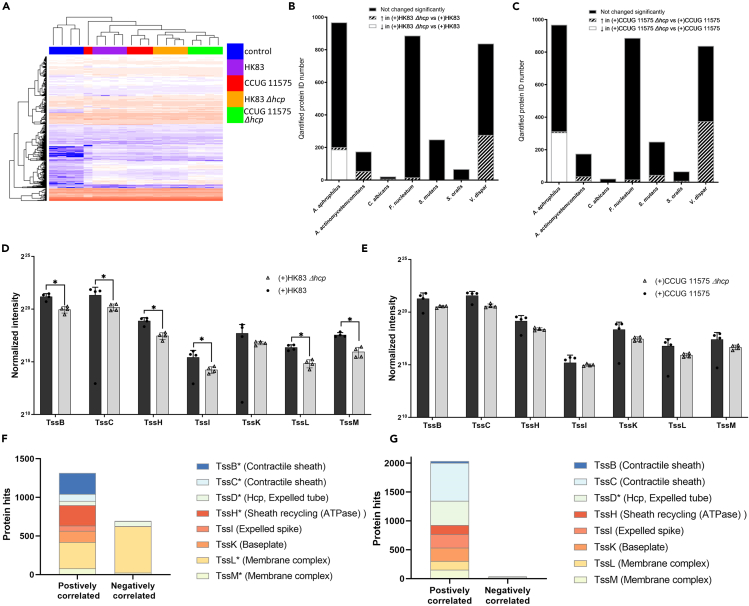
Figure 4.
Metaproteomic shifts in multi-species biofilms
(A) Protein profiles from different biofilms were compared using heatmaps based on unsupervised clustering of label-free quantitation data. The multi-species biofilms included a non-A. aphrophilus control (blue), or an A. aphrophilus strain as follows: HK83 (purple), CCUG 11575 (red), and the hcp mutant strains HK83 Δhcp (yellow), and CCUG 11575 Δhcp (green) as indicated.
(B) The number of regulated proteins in HK83 Δhcp compared with HK83–included multi-species biofilms.
(C) Numbers of regulated proteins in CCUG 11575 Δhcp compare with CCUG 11575 multi-species biofilms. Actinomyces oris proteins were excluded from panels B and C due to the low number of proteins identified from this species (n = 3). In the HK83–containing biofilms, one protein was regulated, i.e., upregulated in HK83 Δhcp biofilms. Conversely, no A. oris protein was regulated in the CCUG 11575-containing biofilms. The normalized abundance of identified T6SS core proteins (excluding Hcp) in multi-species biofilms containing HK83 Δhcp or HK83 (D), and CCUG 11575 Δhcp or CCUG (E), respectively. The number of proteins correlated to T6SS core proteins in HK83 Δhcp or HK83- included in multi-species biofilms (F).
(G) CCUG 11575 Δhcp or CCUG 11575 included in multi-species biofilms.
The results are expressed as means ± standard deviations. The asterisk (∗) denotes the core proteins that have significant differences (p-value<0.05 and abs(log2FC)≥2) between the Δhcp mutated and wild-type-included multi-species biofilms.