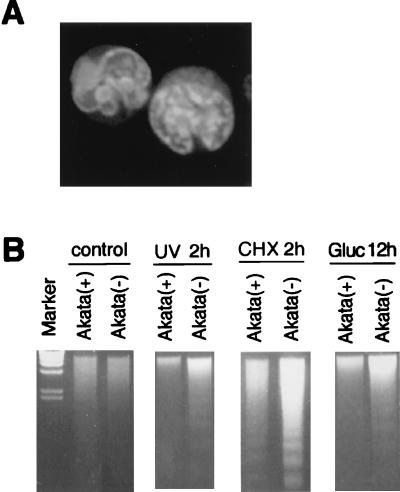
FIG. 3.
Apoptosis in Akata cells. (A) Typical morphology of apoptotic cells induced by cycloheximide in EBV-negative Akata cells. Cells were stained with acridine orange (2 μg/ml) and photographed by laser scanning fluoromicroscopy (Molecular Dynamics). (B) DNA laddering occurs in response to the treatment with UV radiation (UV), cycloheximide (CHX), and glucocorticoid (Gluc). DNA from 4 × 105 cells was subjected to 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and stained with ethidium bromide. Incubation times are given above the gels. The intensity of the DNA ladder of EBV-negative cells [Akata(−)] is stronger than that from EBV-positive cells [Akata(+)], suggesting that EBV-negative cells are more liable to die of apoptosis than are EBV-positive cells.