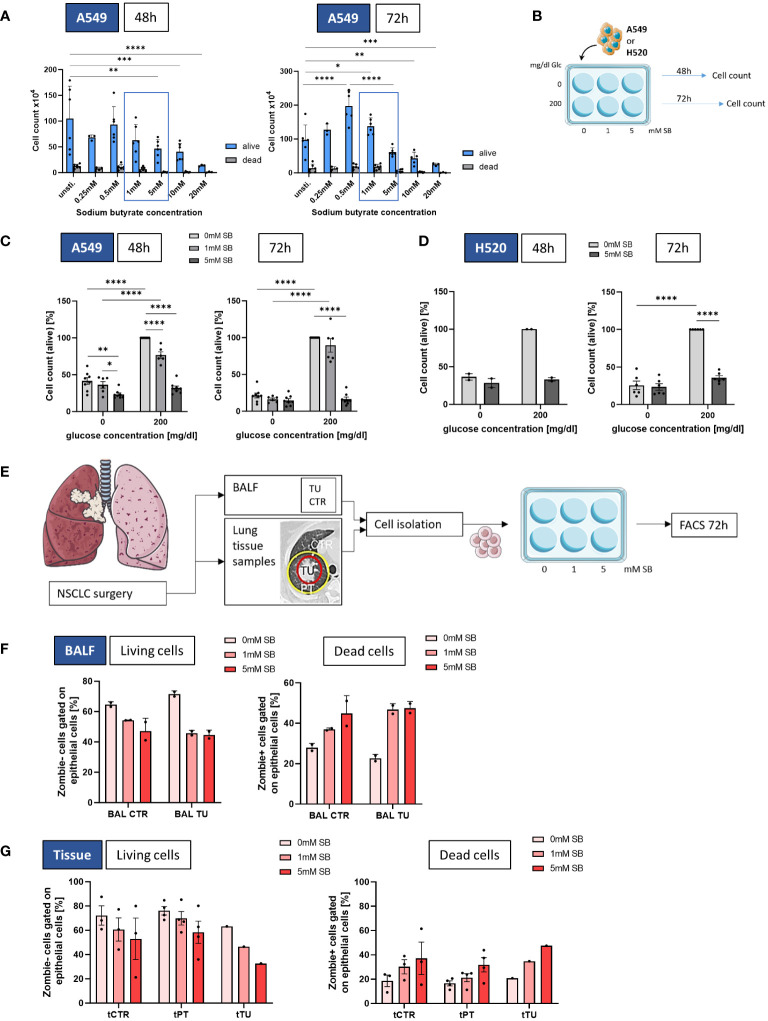
Figure 1.
SB reduced cell viability in lung cancer cell lines A549 and H520, as well as in NSCLC-patient derived epithelial cells. (A) Cell count of living and dead A549 cultured with different SB concentrations (0-20mM SB) after 48h (left panel) and 72h (right panel); (B) Schematic illustration of the experimental design. 5x105 A549 or H520 cells per well were incubated for 48 or 72h with 200mg/dl glucose or without and SB concentrations increased from 0mM over 1mM to 5mM SB; (C) Percentages of the cell count of living A549 cells stained with trypan blue solution after 48h or 72h of SB treatment 48h in relation to the control population (200mg/dl glucose, 0mM SB, (n=8); (D) Percentages of the cell count of living H520 cells stained with trypan blue solution after 48h (n=2) or 72h (n=6) of SB treatment in relation to the control population (200mg/dl glucose, 0mM SB),; (E) Schematic illustration of the experimental design of the human study. BALF- or tissue-derived cells were cultured in collagen coated wells for 72h with increasing SB concentrations from 0mM over 1mM to 5mM SB and analyzed by FACS; (F) Percentages of Zombie- (living) CD326+ epithelial cells or Zombie + (dead) CD326+ epithelial cells cultured from BALF in control regions and tumor regions with different SB concentrations analyzed by flow cytometry, (ncontrol=2; ntumor=2); (G) Percentages of Zombie- (living) CD326+ epithelial cells or Zombie + (dead) CD326+ epithelial cells cultured from lung tissue samples in control, peritumoral and tumor regions with different SB concentrations analyzed by flow cytometry, (ncontrol=3, nperitumoral=4, ntumor=1); (*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; *** P<0.001; ****P < 0.0001). Two-way ANOVA test was used for figure (A), one-way ANOVA test was used for figure (C, D, F, G left panel), Kruskal-Wallis test was used for figure (G right panel). All data are presented as mean values ± SEM.; Parts of the figure were drawn by using pictures from Servier Medical Art and is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).