Fig. 5.
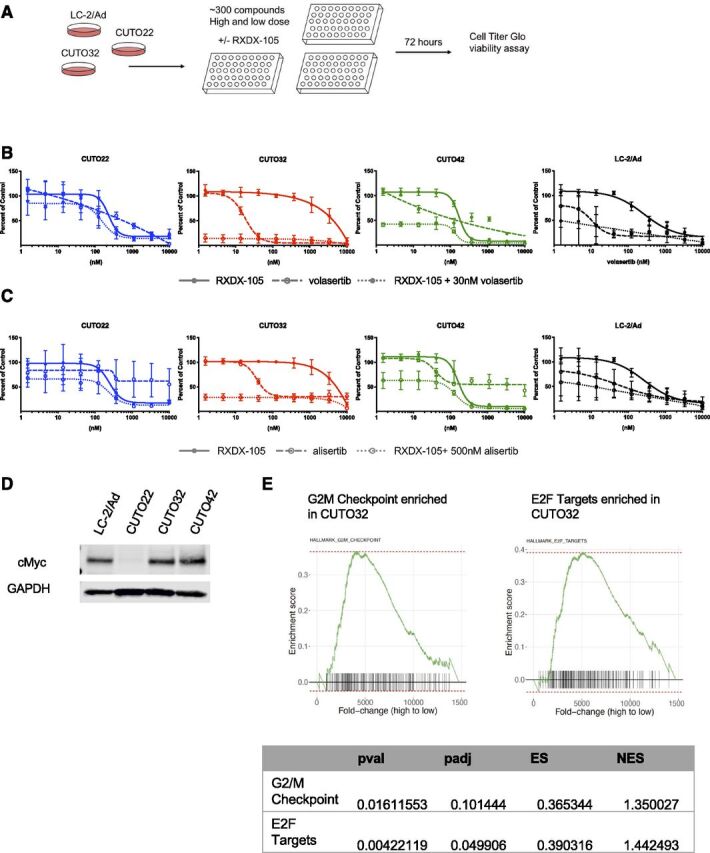
Drug screening reveals unique vulnerabilities in cell cycle regulation. (A) Schematic describing drug screening strategy. CUTO22, CUTO32, and LC-2/Ad cells were treated with approximately 300 compounds at two fixed concentrations of inhibitors with or without 200 nM RXDX-105. Cell viability was assayed after 72 hours using Cell Titer Glo. (B) MTS proliferation assays of CUTO22, CUTO32, CUTO42, and LC-2/Ad cells treated with RXDX-105, volasertib, or RXDX-105 combined with 30 nM volasertib for 72 hours. Error bars represent means ± S.D. for three replicate experiments. (C) MTS proliferation assays of CUTO22, CUTO32, CUTO42, and LC-2/Ad cells treated with RXDX-105, alisertib, or RXDX-105 combined with 500 nM alisertib for 72 hours. Error bars represent means ± S.D. for three biologic replicate experiments. (D) Immunoblot analysis for MYC expression in CUTO22, CUTO32, CUTO42, and LC-2/Ad cells. (E) Gene set enrichment analysis of CUTO32 (untreated) compared with CUTO22 (untreated) cells shows an enrichment of genes associated with G2/M transition and E2F targets in CUTO32 cells. Adjusted p-value (padj), p-value (pval), enrichment score (ES), normalized enrichment score (NES).
