Fig. 6.
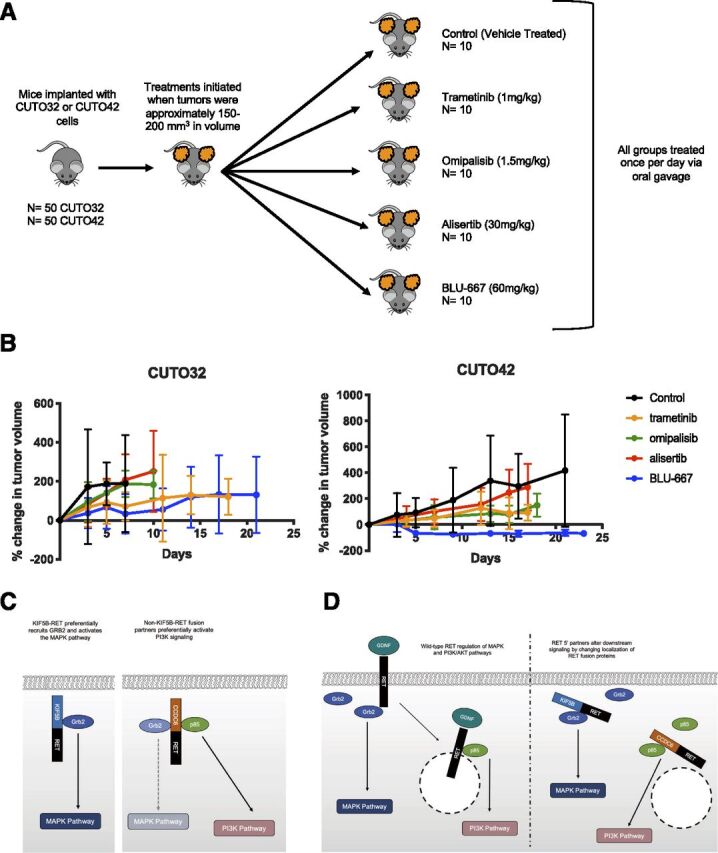
RET inhibitor treatment inhibits tumor growth in CUTO42 xenografts more effectively than CUTO32 xenografts. (A) CUTO32 or CUTO42 cells were subcutaneously implanted in the flanks of nude mice. Once tumors developed, mice were treated once per day with 60 mg/kg BLU-667, 1 mg/kg trametinib, 1.5 mg/kg omipalisib, 30 mg/kg alisertib, or control (vehicle) via daily oral gavage. N = 10 mice per treatment group. (B) Graphs of percent change in tumor growth (relative to starting tumor volume at initiation of treatment). Error bars represent ±S.D. (C) Summary figure describing potential for differential recruitment of adapter proteins in KIF5B-RET+ and non–KIF5B-RET+ cells. (D) Potential differential subcellular localization of RET fusion proteins. Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF), growth factor receptor bound protein 2(Grb2).
