Fig. 1A.
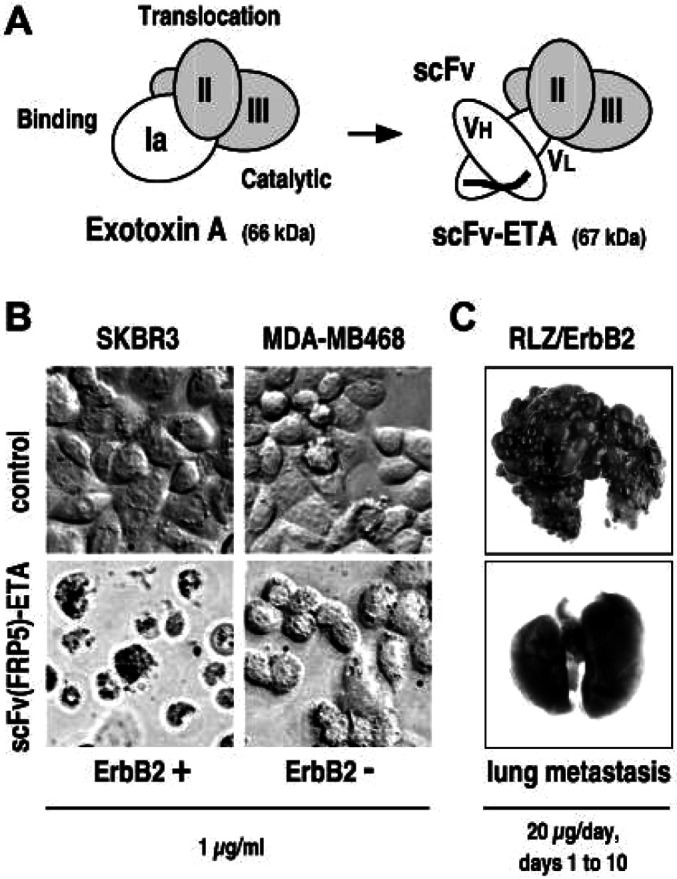
Schematic representation of the structures of Pseudomonas aeruginosa exotoxin A (ETA) and an ETA-based single-chain antibody-toxin. ETA consists of an N-terminal cell binding domain (Ia), an internal translocation domain (II), and a C-terminal enzymatic domain (III) facilitating ADP-ribosylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2. By replacement of domain Ia with a scFv antibody fragment, chimeric antibody-toxins with novel target cell specificity are derived. B Specificity of scFv(FRP5)-ETA antibody-toxin. ErbB2-overexpressing SKBR3 and ErbB2-negative MDA-MB468 human breast carcinoma cells were incubated for 24 h with 1 μg/ml ErbB2-specific scFv(FRP5)-ETA (lower panels) or PBS (upper panels) before analysis by light microscopy. C Antimetastatic activity of scFv(FRP5)-ETA in vivo. Balb/c mice were injected intravenously with 105 murine renal carcinoma (Renca) cells stably transfected with lacZ and human c-erbB2 constructs (RLZ/ErbB2) at day 0. Animals were treated i.v. with 20 µg/dose of scFv(FRP5)-ETA from days 1–10. Control animals received PBS. Mice were sacrificed at day 28, lungs were excised and analyzed for pulmonary metastasis upon X-gal staining [27]
