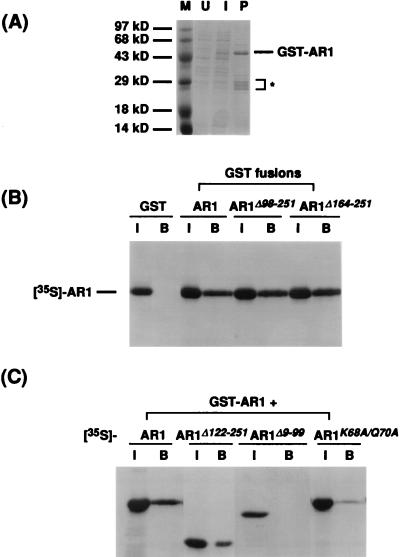
FIG. 9.
AR1-AR1 in vitro binding assay. (A) Induction and purification of GST-AR1 from E. coli. GST-AR1 was purified from E. coli extracts by binding to and elution from glutathione-Sepharose beads. U, lysate from uninduced bacteria; I, lysate from bacteria induced with IPTG; P, GST-AR1 fusion protein bound to and eluted from glutathione-Sepharose beads. The position of the GST-AR1 fusion protein was verified by immunoblotting with anti-AR1 antiserum (data not shown). The asterisk indicates GST-AR1 degradation products. Sizes of protein molecular mass markers (M) are indicated. See text for details. (B) Binding of wild-type AR1 to GST, GST-AR1, and C-terminal truncations of AR1 fused to GST (GST-AR1Δ98-251 and GST-AR1Δ164-251). [35S]methionine-labeled in vitro-synthesized wild-type AR1 protein was incubated with the GST fusion proteins, as indicated, bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads. Shown are SDS-polyacrylamide gels of labeled AR1 bound. I, input [35S]methionine-labeled AR1; B, bound [35S]methionine-labeled AR1. (C) Binding of [35S]methionine-labeled AR1, AR1Δ122-251, AR1Δ9-99, and AR1K68A/Q70A to GST-AR1. In vitro-transcribed and -translated wild-type or mutant AR1 (as indicated) was incubated with GST-AR1 bound to glutathione-Sepharose beads. Shown are SDS-polyacrylamide gels of each AR1 protein bound. I, input [35S]methionine-labeled AR1 wild-type or mutant protein; B, bound [35S]methionine-labeled AR1 wild-type or mutant protein.