Fig. 7.
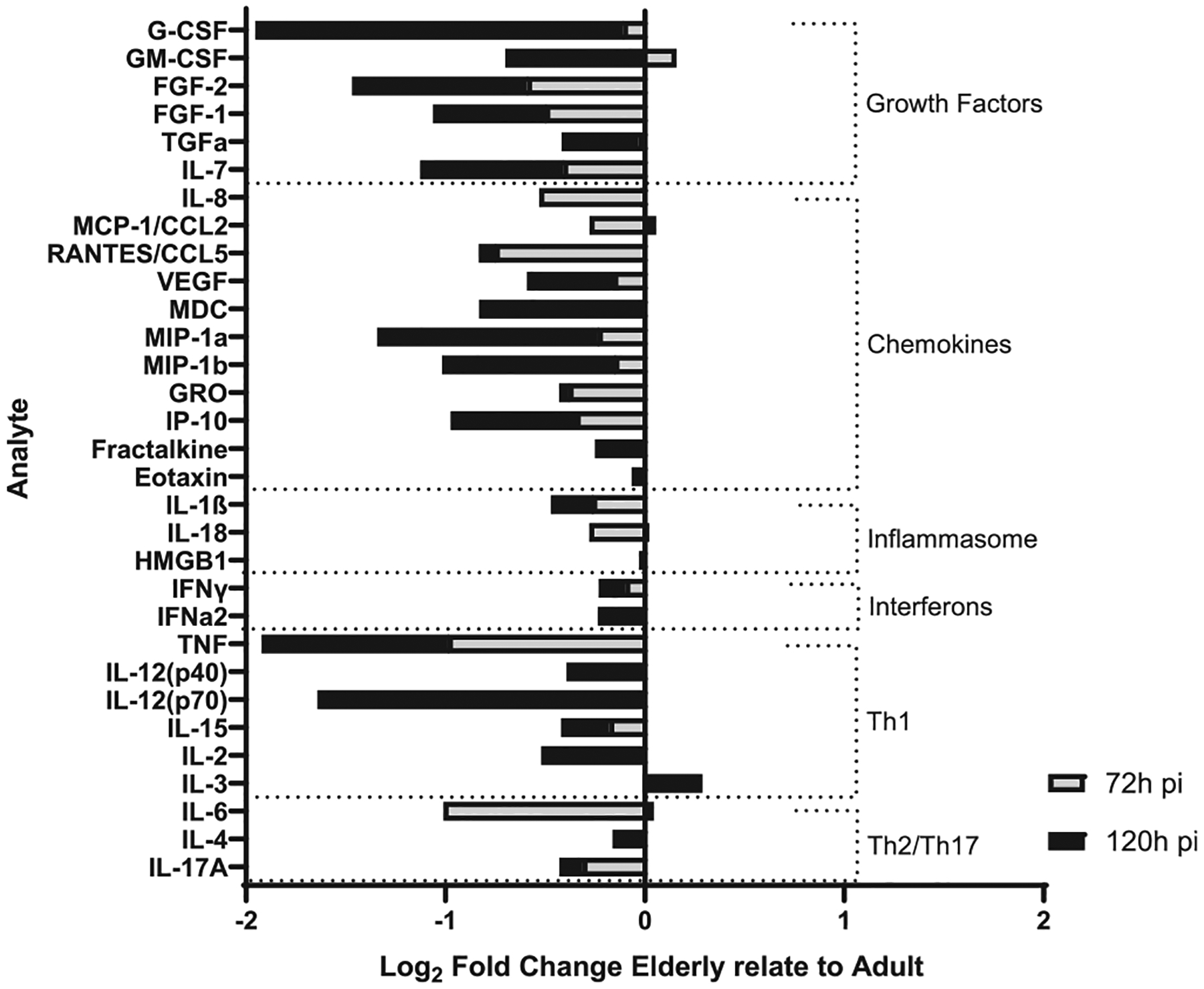
E-ALF-exposed M.tb drives a decrease in production of ATs immune mediators. ATs were infected with either A-ALF or E-ALF-exposed M.tb for 2 hours at MOI of 100:1 followed by 1 hour of gentamicin to kill extracellular M.tb. AT supernatants from infected ATs with either A-ALF-exposed or E-ALF-exposed M.tb were assessed for growth factors, cytokines, and chemokines production and measured at 72 hpi and 120 hpi by multiplexed biomarker assay following the manufacturer’s instructions. The graph shows the log2 fold changes of supernatants from E-ALF-exposed M.tb infected ATs relative to A-ALFs; and categorized into the following groups: growth factors, chemokines, inflammasome, interferons, Th1 and Th2/Th17 mediators. Values correspond to log2 (median total [pg/ml] E-ALF / median total [pg/ml] A-ALF) for n = 4, using pooling of four different A-ALF or E-ALF donors from three separate experiments. A = adult ALF-exposed M.tb; ALF = alveolar lining fluid; ATs = alveolar epithelial type cells; E = elderly ALF-exposed M.tb; hpi = hours post-infection; MOI = multiplicity of infection; M. tb = Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Th = T helper cell mediators.
