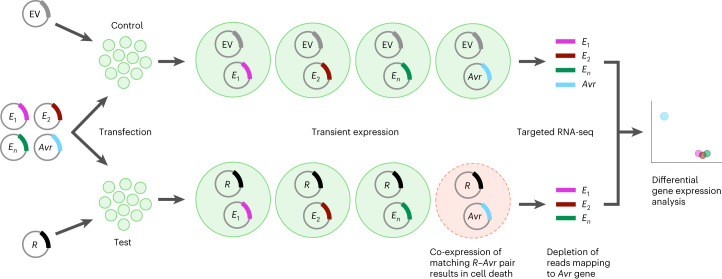
Fig. 1. Schematic of pooled effector library screening process to identify interacting R–Avr pairs.
Protoplast populations are co-transformed with a pooled library comprising hundreds of effector genes (E1, E2, En, Avr) from a pathogen along with either a known R gene or an empty vector (EV) for the negative control. The library MOT, defined as the number of plasmid molecules per cell (for each library construct), is chosen such that each library construct is expressed in an independent subpopulation of cells. Each cell individually receives a random but limited number of different constructs from the library together with either the empty vector or the R gene. In the presence of the R gene, protoplasts that express a matching Avr effector gene undergo cell death, while cells expressing the same Avr effector gene in the negative control remain alive. Living protoplasts are subsequently collected from both transformed populations and subjected to targeted (library-specific) RNA-seq. The expression of each effector in the library is then compared between the two samples (differential gene expression analysis). Avr gene candidates are identified by their decreased expression in the sample expressing the corresponding R gene.