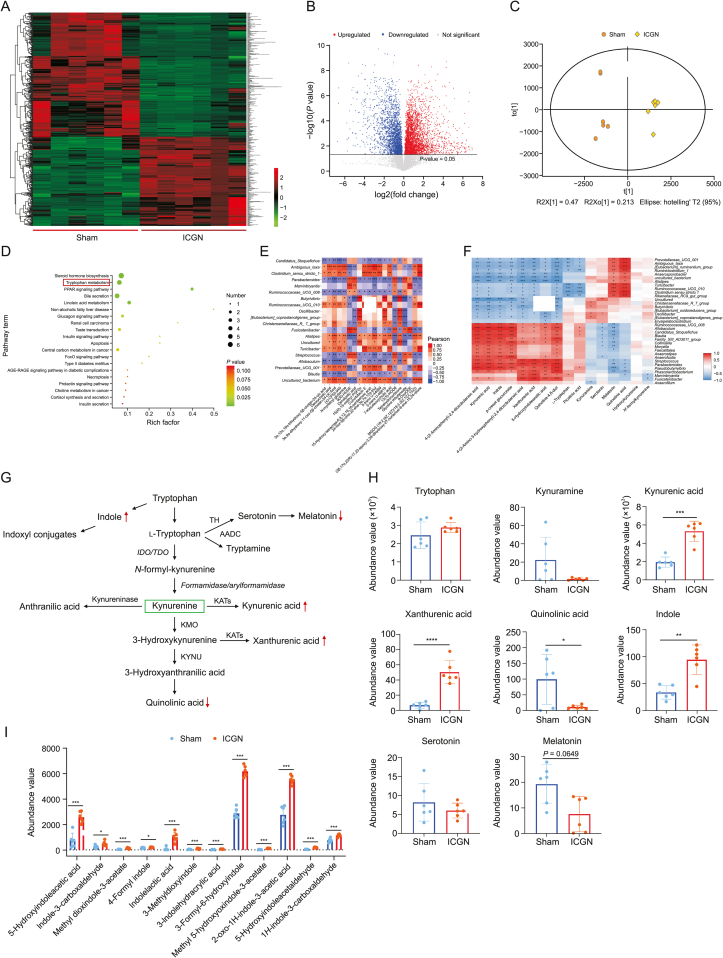
Fig. 4.
Alteration of fecal metabolome in immune-complex glomerulonephritis (ICGN) rats. (A) Heatmap showing the differences in the distribution of metabolites between the model and control groups. (B) Volcano plot showing the differences in the distribution of metabolites between the model and control groups. (C) Score plots of orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA) showing that ICGN rats can be clearly differentiated from the rats in the sham group. (D) Enriched Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathways of differential metabolites between sham and ICGN rats. (E) Spearman correlation analysis between the top 20 abundant differential genera and the top 20 abundant differential metabolites. (F) Heatmap of correlation analysis between differentially tryptophan catabolites and differential genera. (G) The three major tryptophan metabolic pathways. (H) Metabolites with significant changes in the tryptophan metabolism pathway between the sham and ICGN groups (n = 6). (I) Comparison of the abundance values of indoxyl conjugates derived from tryptophan metabolism (n = 6). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, and ∗∗∗∗P < 0.0001 by analysis of variance (ANOVA) (n = 10). PPAR: peroxisome proliferators-activated receptors; FoxO: Forkhead box O; ARE-RAGE: advanced glycation end-products-receptor of advanced glycation endproducts; CP 55,940: 5-(1,1-dimethylheptyl)-2-[5-hydroxy-2-(3-hydroxypropyl)cyclohexyl]phenol; HODE: hydroxy-10E,12Z-octadecadienoic acid; PGF: prostaglandin F; OxoODE: oxo-10,12-octadecadienoic acid; MGDG: monogalactosyldiacylglycerol; TH: tyrosine hydroxylase; AADC: aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase; IDO/TDO: indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase/tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase gene; KATs: K(lysine) acetyltransferase; KMO: kynurenine 3-monooxygenase; KYNU: kynureninase.