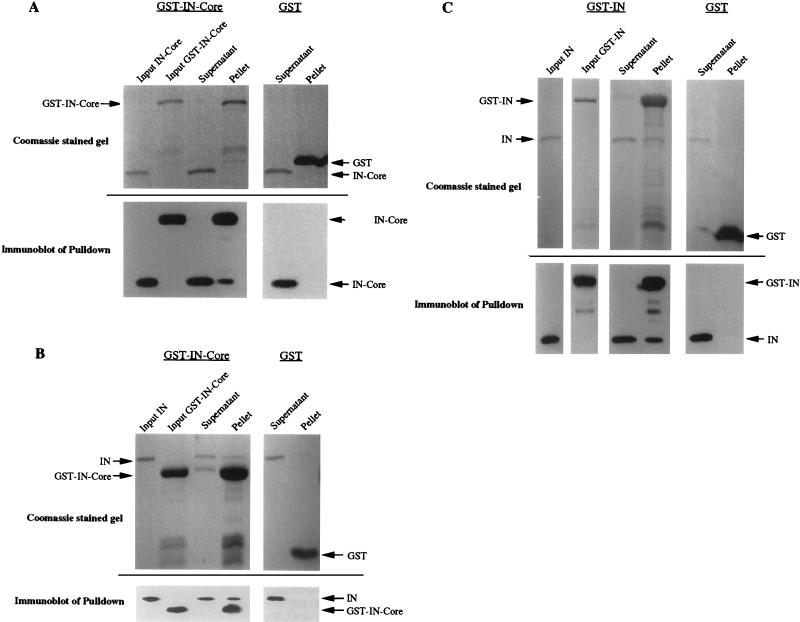
FIG. 3.
In vitro binding between IN and IN-core proteins. IN and IN-core proteins were expressed as GST fusion proteins in bacteria and were purified by binding to glutathione-Sepharose 4B beads (Pharmacia Biotech). One set of proteins bound to resin was cleaved from GST with Prescission protease (Pharmacia Biotech) at 4°C for 2 to 4 h in the presence of cleavage buffer containing 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.0), 150 mM NaCl, 1 mM EDTA, and 1 mM dithiothreitol. For binding experiments, cleaved proteins were isolated and incubated with Sepharose 4B beads bound to GST-fused IN or IN-core (containing a factor Xa cleavage site) at 22°C for 45 min in the presence of binding buffer containing 1× phosphate-buffered saline, 0.1% Tween 20, and 0.1% Casamino Acids. The binding buffer was used to wash the beads four times to remove unbound proteins. The beads were then boiled in 2× sample buffer, and the proteins bound to the GST fusion proteins were analyzed by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting with anti-IN antisera (28). (A) Pulldown of IN-core by GST-IN-core. Five percent of the input of IN-core and GST-IN-core and 10% of the supernatant and pellet were loaded on the Coomassie blue-stained gel. Approximately one-fourth of each of these samples was then run on a separate gel and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane for immunoblotting with anti-IN antisera. (B) Pulldown of IN by GST-IN-core. The same amounts of samples as described above were loaded. (C) Pulldown of IN by GST-IN. Again, 5% of the input of cleaved IN was loaded along with 10% of the supernatant and pellet from each pulldown.