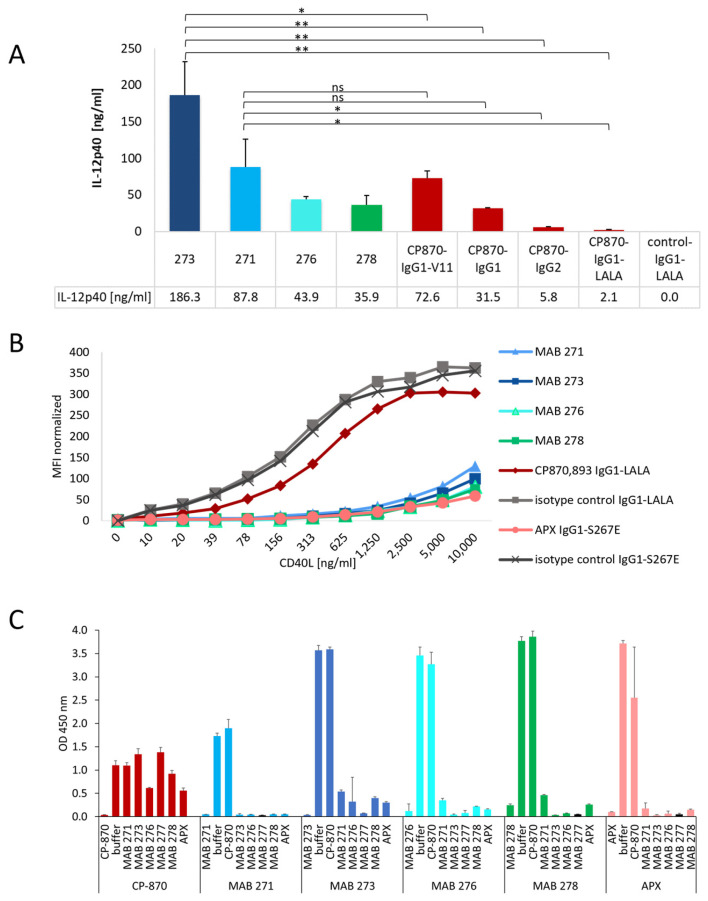
Figure 2.
Differentiation of novel Fcγ-receptor-independent anti-CD40 antibodies from other clinical antibodies. (A) The activity of the four most active CD40 hIgG1-LALA antibodies, MAB 271, 273, 276 and 278, were tested for the activation of in vitro differentiated DCs in direct comparison to different Fc-variants of CP-870,893. IL-12p40, released by DCs, was measured by ELISA. The statistical significance for difference between MAB 273, MAB 271 and the Fc-variants of CP-870,893 was determined by an unpaired t-test. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, ns = not significant. (B) CD40 antibodies were incubated with CD40-expressing HEK-Blue-CD40L™ cells, and interference with CD40L binding to CD40 was tested by the addition of increasing concentrations of recombinant CD40L-mIgG2a-Fc-fusion protein. The binding of CD40L was detected by flow cytometry using a fluorescently labeled anti-mouse IgG antibody. (C) The competition of anti-CD40 antibodies for binding to human CD40 was tested in a sandwich ELISA. Each antibody was tested both as a coating (vertical label) and as a detection antibody (horizontal label) in combination with any other anti-CD40 antibody. Error bars in (A,C) indicate the standard deviation (mean) of triplicates.