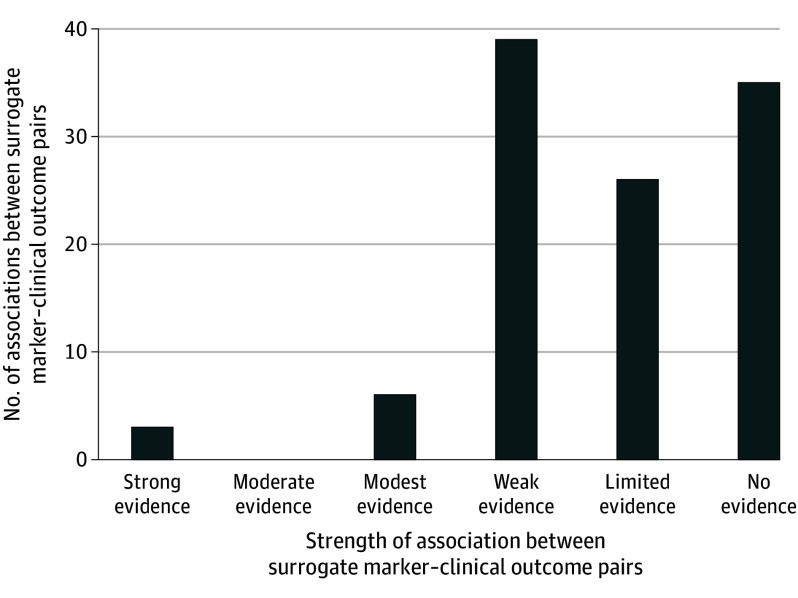
Figure 3. Strength of the Associations Between 109 Surrogate Marker–Clinical Outcome Pairs.
Strong evidence: correlation coefficients or coefficients of determination values reported for all associations examined, and all associations classified as statistically significant and high strength according to criteria proposed by the Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (r ≥ 0.85 or R2 ≥ 0.72).14 Moderate evidence: r or R2 values reported for all associations examined, and 1 or more (but not all) classified as statistically significant and high strength. Modest evidence: r or R2 values reported for some associations examined, and 1 or more (but not all) classified as statistically significant and high strength. Any other r, R2, slopes, effect estimates, or results from meta-regression analyses classified as statistically significant. Weak evidence: no r or R2 values classified as both statistically significant and high strength, but all r, R2, slopes, effect estimates, or results from meta-regression analyses classified as statistically significant. Limited evidence: no r or R2 values classified as both statistically significant and high strength; some r, R2, slopes, effect estimates, or results from meta-regression analyses classified as statistically significant and some not. No evidence: no r or R2 values classified as statistically significant and high strength, and all r, R2, slopes, effect estimates, or results from meta-regression analyses classified as nonstatistically significant.