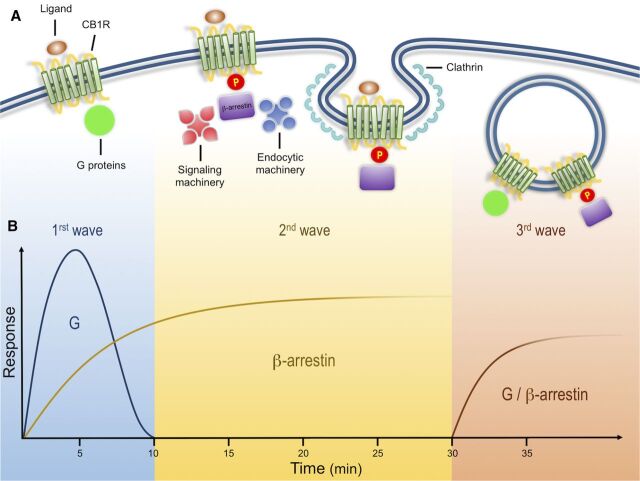
Fig. 1.
Cannabinoid receptor signals in three waves. (A) Activation of CB1Rs results in the modulation of multiple cellular responses through three distinct signaling waves. The first wave, mediated by G proteins, is observed within seconds and up to few minutes after receptor activation. Receptor activation also results in phosphorylation by GRKs. This post-translational modification leads to receptor desensitization and the recruitment of β-arrestins, scaffold proteins of the endocytic machinery that initiate clathrin-mediated endocytosis. In addition to the endocytic machinery, receptor bound β-arrestins can also recruit and activate signaling proteins, resulting in a second signaling wave with distinct kinetic and signaling profile. These events are initiated at the plasma membrane and can continue after receptor endocytosis into intracellular compartments. After receptor internalization, a third signaling wave has been described that is characterized by the activation of effectors associated with both G proteins and β-arrestins. (B) Proposed time course of G protein– and β-arrestin–mediated responses. G protein signaling has a fast initial response, whereas β-arrestins are somewhat slower but sustained over time. Kinetics of third waves can be initiated within minutes (modified from Luttrell and Gesty-Palmer, 2010).